
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 536
Question Number 166737 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 166735 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 166725 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
$$\:\:\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{tan}\:\mathrm{x}}=? \\ $$
Question Number 166723 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166719 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 166718 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${csc}\mathrm{10}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}{sec}\mathrm{10}=? \\ $$
Question Number 166715 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166707 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166702 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 166701 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
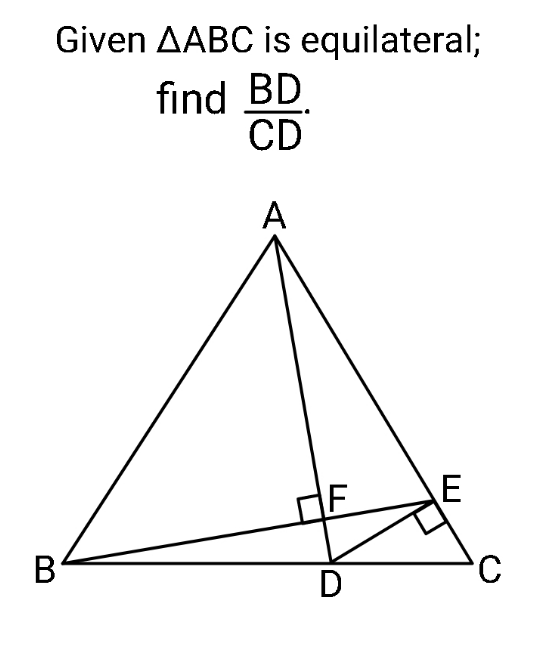
Question Number 166699 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166697 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 166690 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166687 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 166686 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 166685 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 166684 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 166683 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 166678 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166676 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
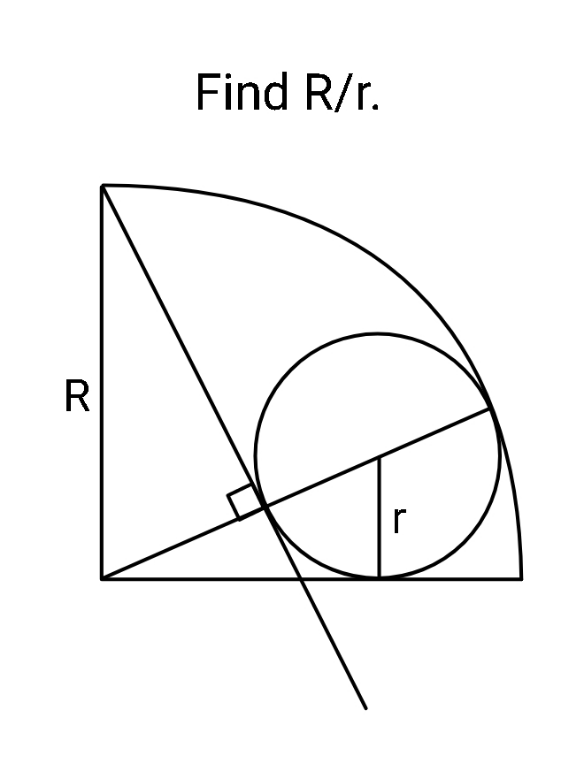
Question Number 166670 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 166695 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 166693 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 166660 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 166649 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
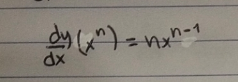
Question Number 166648 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 531 Pg 532 Pg 533 Pg 534 Pg 535 Pg 536 Pg 537 Pg 538 Pg 539 Pg 540
