
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 532
Question Number 167126 Answers: 0 Comments: 9
Question Number 167122 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 167119 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 167115 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 167110 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 167107 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 167105 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
Question Number 167102 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 167100 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 167092 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 167091 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 167120 Answers: 3 Comments: 0

Question Number 167086 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
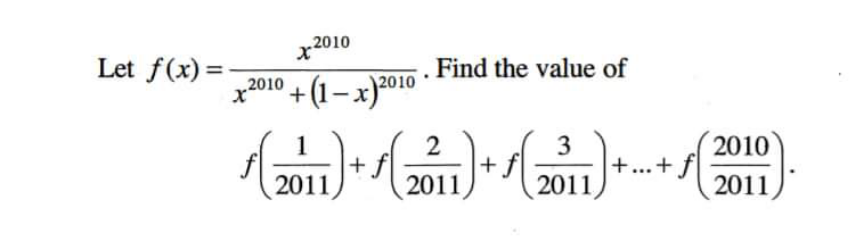
Question Number 167085 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 167082 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 167078 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 167077 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 167073 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 167067 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 167066 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 167058 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 167056 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 167048 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 167054 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 167043 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
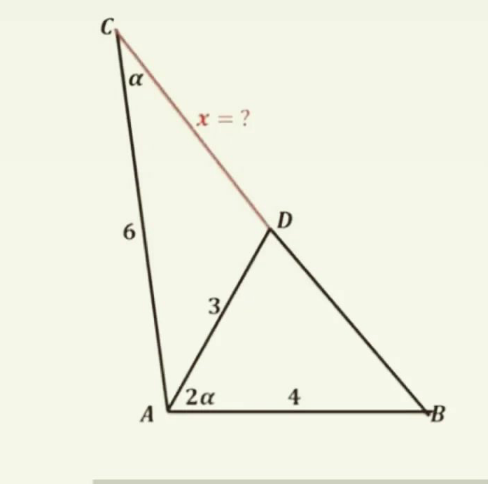
Question Number 167040 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 527 Pg 528 Pg 529 Pg 530 Pg 531 Pg 532 Pg 533 Pg 534 Pg 535 Pg 536
