
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 508
Question Number 169349 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 169347 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
Question Number 169346 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 169342 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 169340 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 169432 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 169333 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 169319 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 169317 Answers: 2 Comments: 3

Question Number 169315 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 169308 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
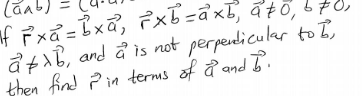
Question Number 169305 Answers: 4 Comments: 2
Question Number 169304 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
Question Number 169303 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 169295 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 169294 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 169291 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
Question Number 169287 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 169281 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
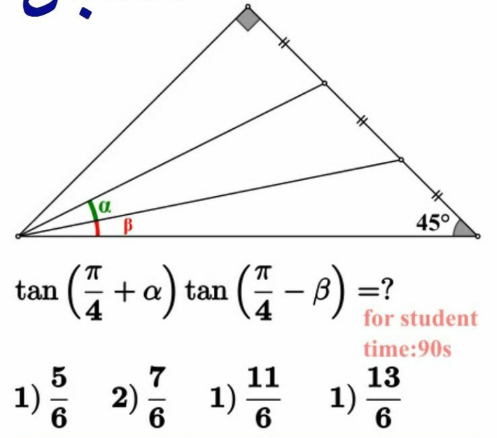
Question Number 169280 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 169273 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 169272 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 169271 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 169268 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 169260 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 169259 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Pg 503 Pg 504 Pg 505 Pg 506 Pg 507 Pg 508 Pg 509 Pg 510 Pg 511 Pg 512
