
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 440
Question Number 176056 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 176060 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Question Number 176054 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 176049 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 176037 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 176035 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 176022 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
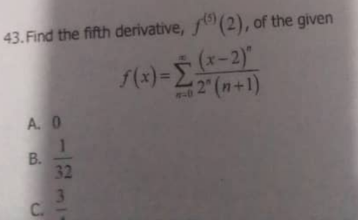
Question Number 176014 Answers: 3 Comments: 1

Question Number 176090 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
$${determiner}\:{z}\:{tel}\:{que}\:{z}={z}^{\mathrm{2}} −{z}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Question Number 176005 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 175996 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{m}}\frac{{a}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}}=? \\ $$
Question Number 175995 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{m}}\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{3}{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}}=? \\ $$
Question Number 175994 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{m}}\frac{{e}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}}=? \\ $$
Question Number 175987 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
Question Number 175986 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 175976 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 175972 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 175967 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 175961 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 175959 Answers: 3 Comments: 2
Question Number 175956 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 175954 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 175953 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 175952 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 175951 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 175949 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Pg 435 Pg 436 Pg 437 Pg 438 Pg 439 Pg 440 Pg 441 Pg 442 Pg 443 Pg 444
