
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 257
Question Number 196518 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 196517 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196516 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196515 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 196504 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 196498 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196496 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196493 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
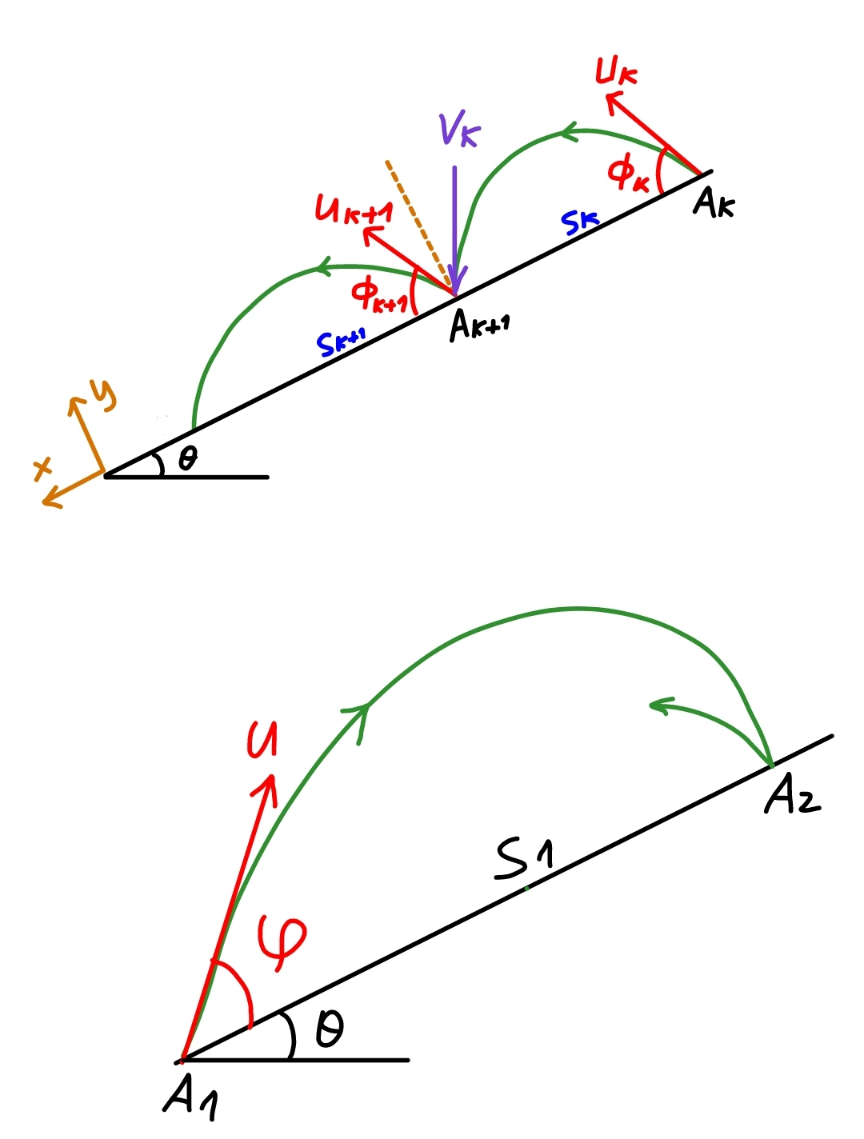
Question Number 196491 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 196489 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 196487 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\left(\mathrm{sec}\:^{\mathrm{4}} {x}−\mathrm{cot}\:^{\mathrm{4}} {x}\right){dx} \\ $$
Question Number 196486 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 196485 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\underset{{k}={o}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{k}} \:=? \\ $$
Question Number 196483 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 196471 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 196467 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196490 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 196464 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 196460 Answers: 1 Comments: 5

Question Number 196459 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196458 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 196447 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 196444 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 196440 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${prove}\:\mid{v}−{w}\mid\geqslant\mid{v}\mid−\mid{w}\mid \\ $$
Question Number 196436 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}\left({x}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$
Question Number 196435 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Pg 252 Pg 253 Pg 254 Pg 255 Pg 256 Pg 257 Pg 258 Pg 259 Pg 260 Pg 261
