
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 193
Question Number 202448 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 202447 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 202436 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 202419 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 202418 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 202415 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 202408 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 202406 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 202400 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 202395 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 202393 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 202392 Answers: 2 Comments: 11
Question Number 202390 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 202388 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 202383 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 202376 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 202374 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
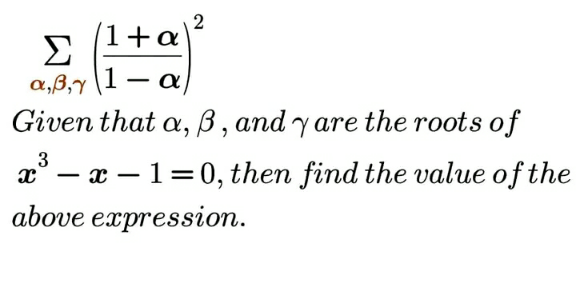
Question Number 202371 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 202359 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 202356 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
Question Number 202353 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 202352 Answers: 0 Comments: 9

Question Number 202348 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 202340 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 202329 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 202328 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Pg 188 Pg 189 Pg 190 Pg 191 Pg 192 Pg 193 Pg 194 Pg 195 Pg 196 Pg 197
