
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1916
Question Number 18527 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 18524 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 18523 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 18502 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18498 Answers: 5 Comments: 1
Question Number 18499 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 18493 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 18492 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 18486 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 18477 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 18474 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18472 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18466 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18465 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18464 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18463 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18461 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 18460 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 18457 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18456 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18455 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18450 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 18448 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 18446 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
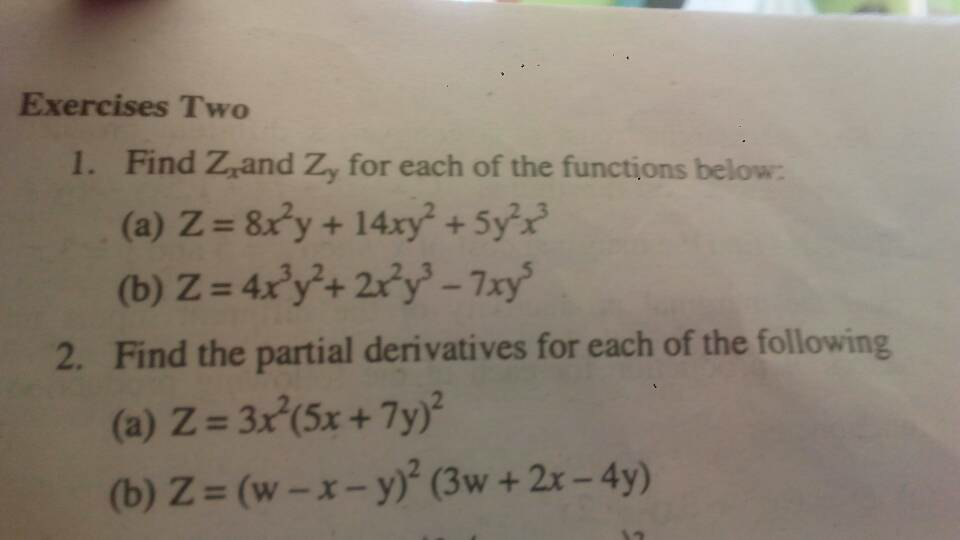
Question Number 18440 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 18439 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Pg 1911 Pg 1912 Pg 1913 Pg 1914 Pg 1915 Pg 1916 Pg 1917 Pg 1918 Pg 1919 Pg 1920
