
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1907
Question Number 19506 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19505 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19531 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 19557 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
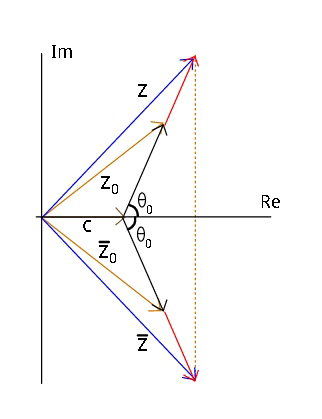
Question Number 19556 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 19499 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19554 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 19472 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 19455 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19435 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19434 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19433 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19419 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19415 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19413 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19409 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 19403 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19457 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${prove}\:{that}\:\int\mathrm{tan}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {xdx} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$=\mathrm{tan}\:{x}−{x} \\ $$
Question Number 19394 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
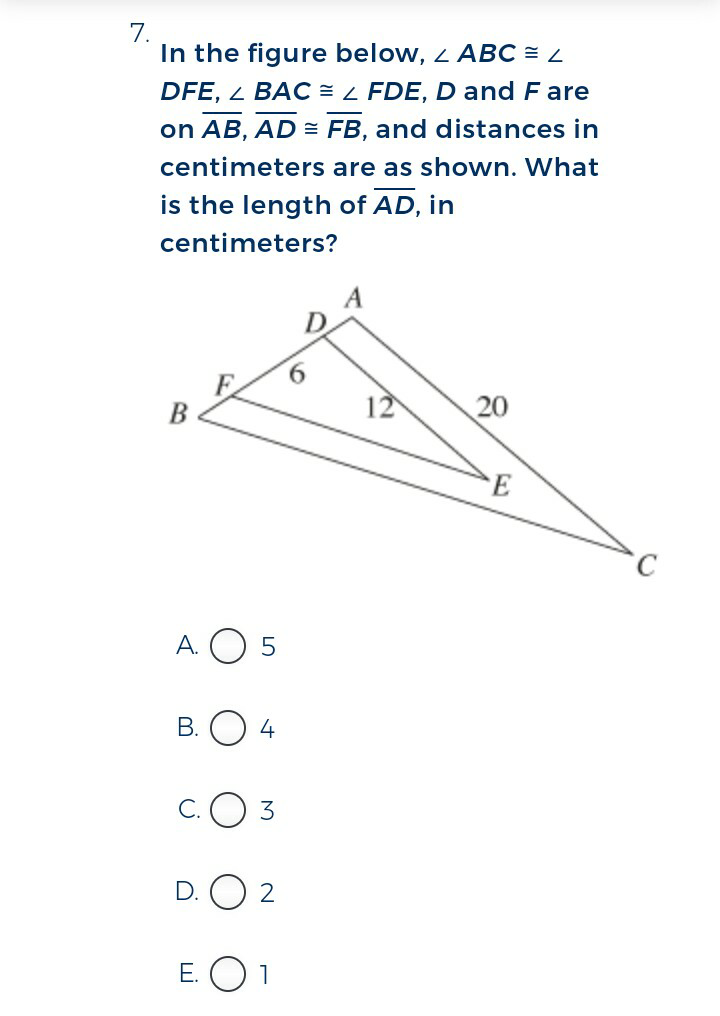
Question Number 19393 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19555 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19391 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 19389 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19388 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 19385 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 19382 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Pg 1902 Pg 1903 Pg 1904 Pg 1905 Pg 1906 Pg 1907 Pg 1908 Pg 1909 Pg 1910 Pg 1911
