
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1857
Question Number 25334 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25335 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 25328 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 25367 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
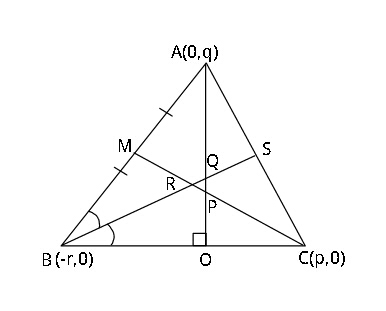
Question Number 25317 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 25315 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 25314 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 25313 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25308 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25307 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 25350 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 25300 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 25295 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25310 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 25290 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\int\frac{{x}\:{dx}}{\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }} \\ $$
Question Number 25288 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 25287 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${limit}_{{x}−\mathrm{0}^{−} } \mathrm{sin}\:\left({log}_{{e}} {x}\right) \\ $$
Question Number 25283 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 25280 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25275 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 25273 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 25254 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25253 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 25252 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 25251 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 25246 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1852 Pg 1853 Pg 1854 Pg 1855 Pg 1856 Pg 1857 Pg 1858 Pg 1859 Pg 1860 Pg 1861
