
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1807
Question Number 30032 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 29953 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
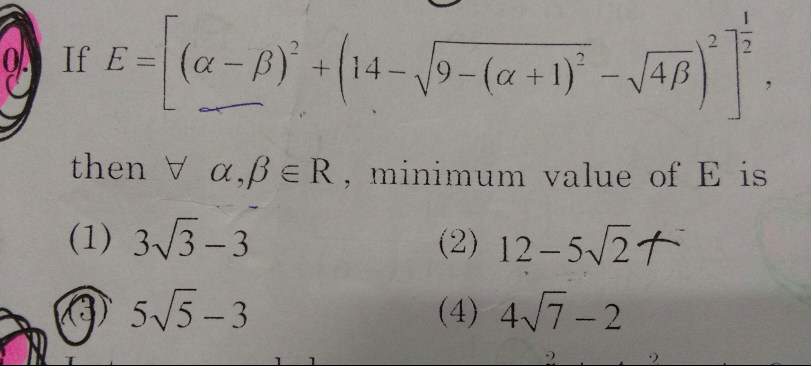
Question Number 29924 Answers: 1 Comments: 5
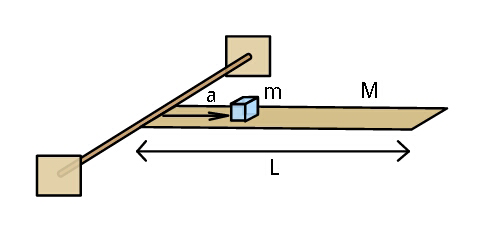
Question Number 29909 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
$${please}\:{solve}\:{this}:\:\:\sqrt{\mathrm{30}+\mathrm{12}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}} \\ $$
Question Number 29907 Answers: 1 Comments: 5

Question Number 29896 Answers: 5 Comments: 1

Question Number 30655 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 29880 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
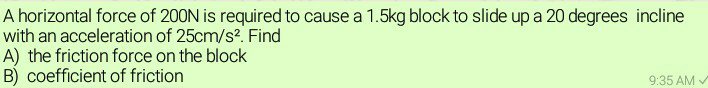
Question Number 29875 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29877 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 29857 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29856 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29855 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 29854 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29853 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29852 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29851 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29850 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29849 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29848 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29847 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29846 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29845 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 29844 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29842 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29841 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 1802 Pg 1803 Pg 1804 Pg 1805 Pg 1806 Pg 1807 Pg 1808 Pg 1809 Pg 1810 Pg 1811
