
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1803
Question Number 30190 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 30189 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 30188 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 30187 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${solve}\:{xy}^{'} \:−\mathrm{2}{y}\:=\:{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:. \\ $$
Question Number 30186 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${solve}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{''} \:−\mathrm{2}{y}\:={x} \\ $$
Question Number 30185 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 30184 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 30183 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 30182 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 30181 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\:\int\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }\:. \\ $$
Question Number 30180 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 30179 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${find}\:\:\int\:\:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+{cost}\:+{sint}}\:\:. \\ $$
Question Number 30178 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 30177 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 30176 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 30175 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 30174 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 30193 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 30166 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
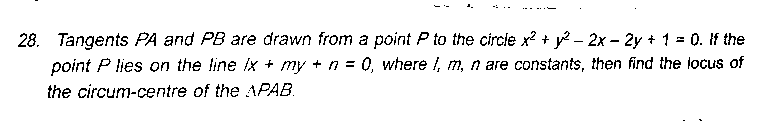
Question Number 30165 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 30160 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 30159 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
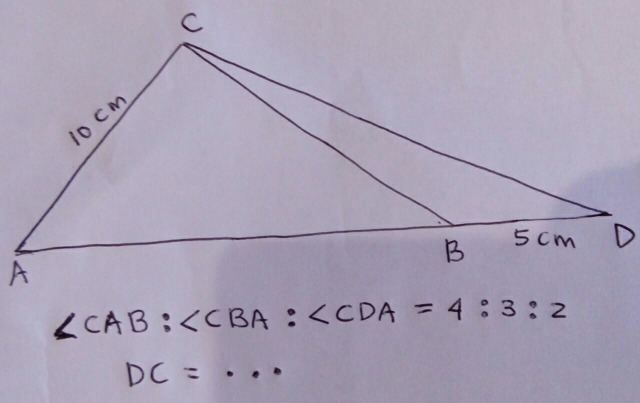
Question Number 30156 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 30148 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 30129 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 30123 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Pg 1798 Pg 1799 Pg 1800 Pg 1801 Pg 1802 Pg 1803 Pg 1804 Pg 1805 Pg 1806 Pg 1807
