
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1767
Question Number 33026 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 33009 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 33005 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32999 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
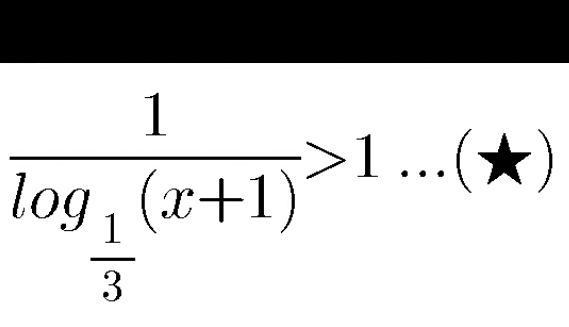
Question Number 32998 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32997 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32996 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32995 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32994 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32993 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 32992 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 32991 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 32990 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\:\:{find}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:{x}\:{e}^{−{lnx}} \:\:. \\ $$
Question Number 32989 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 32987 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 32985 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
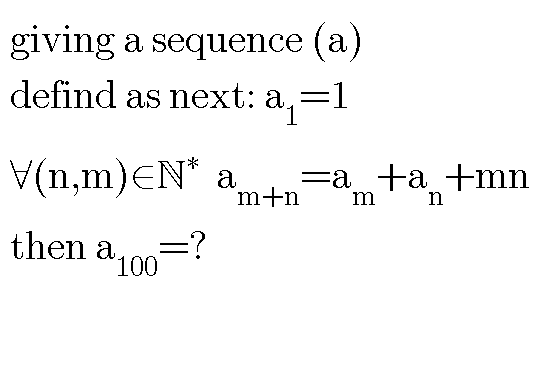
Question Number 32980 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 33152 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32977 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 33125 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 33124 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 32971 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 32968 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
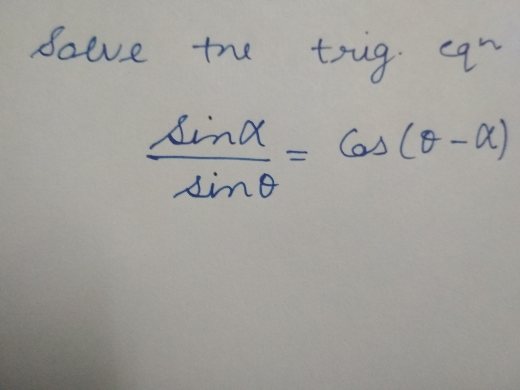
Question Number 32958 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
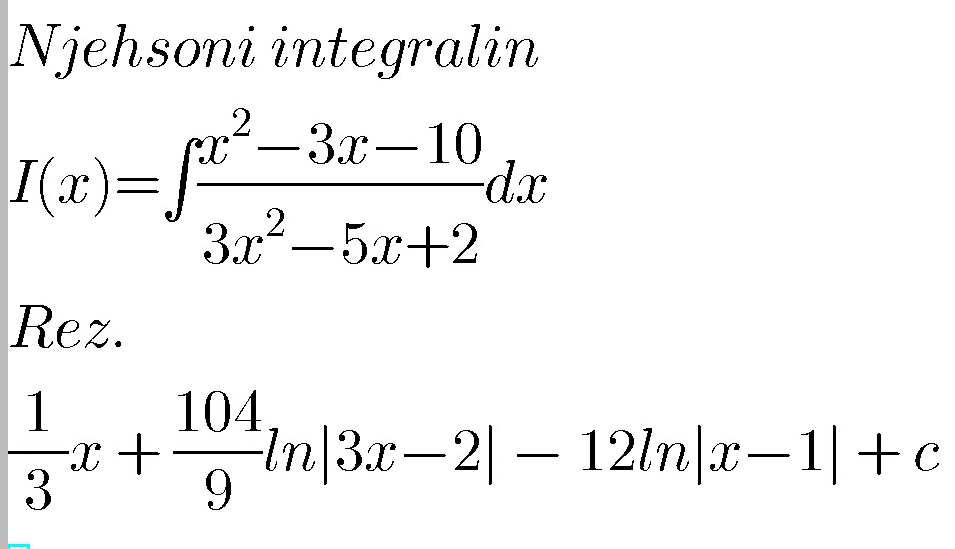
Question Number 32954 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 32951 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Pg 1762 Pg 1763 Pg 1764 Pg 1765 Pg 1766 Pg 1767 Pg 1768 Pg 1769 Pg 1770 Pg 1771
