
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1714
Question Number 37447 Answers: 2 Comments: 5
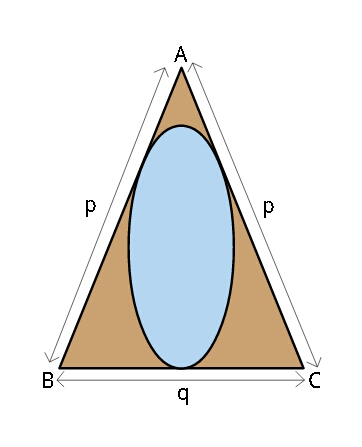
Question Number 37432 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 37425 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 37424 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 37422 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 37630 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 37414 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${x}^{{x}} =\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}. \\ $$
Question Number 37411 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\left(\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{2}\right)^{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} }\right. \\ $$
Question Number 37404 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 37382 Answers: 2 Comments: 3
Question Number 37367 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 37366 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 37365 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37364 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37363 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${solve}\:{y}^{'} \:\:+{xe}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {y}\:\:={e}^{−{x}} \:\:. \\ $$
Question Number 37362 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37361 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 37360 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$
Question Number 37359 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37357 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 37356 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 37355 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 37354 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37353 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37352 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 37350 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Pg 1709 Pg 1710 Pg 1711 Pg 1712 Pg 1713 Pg 1714 Pg 1715 Pg 1716 Pg 1717 Pg 1718
