
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1702
Question Number 38870 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${i}\:{am}\:{posting}\:{what}\:{i}\:{think}\:{helpful}... \\ $$
Question Number 38865 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38864 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38863 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38862 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38861 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38860 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38859 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38858 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38857 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38856 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38855 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38854 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38853 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 39030 Answers: 2 Comments: 3
Question Number 38849 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 38847 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38836 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 38825 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
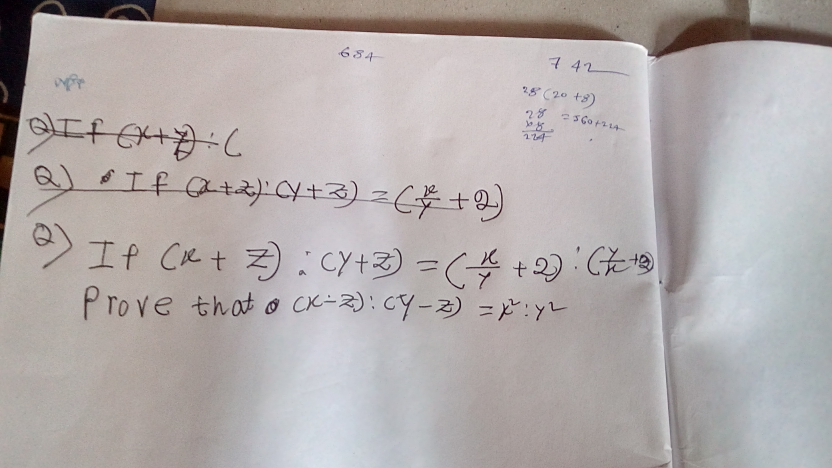
Question Number 38822 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 38816 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 38812 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 38804 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 38802 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 39029 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 38786 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Pg 1697 Pg 1698 Pg 1699 Pg 1700 Pg 1701 Pg 1702 Pg 1703 Pg 1704 Pg 1705 Pg 1706
