
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1697
Question Number 39388 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 39386 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 39384 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 39383 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 39382 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 39381 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 39380 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 39379 Answers: 1 Comments: 6

Question Number 39378 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 39376 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 39375 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 39374 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 39373 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 39371 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
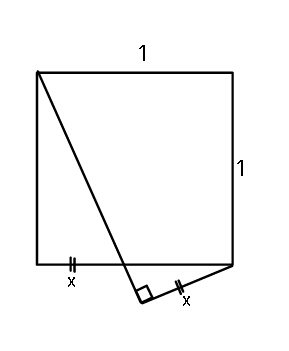
Question Number 39370 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 39369 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 39368 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 39365 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 39357 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{xln}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\:{dx} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Question Number 39349 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 39346 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 39342 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 39341 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 39338 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 39336 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 39337 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 1692 Pg 1693 Pg 1694 Pg 1695 Pg 1696 Pg 1697 Pg 1698 Pg 1699 Pg 1700 Pg 1701
