
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1683
Question Number 40830 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${find}\:\int\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}+{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}}{dt} \\ $$
Question Number 40829 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40826 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
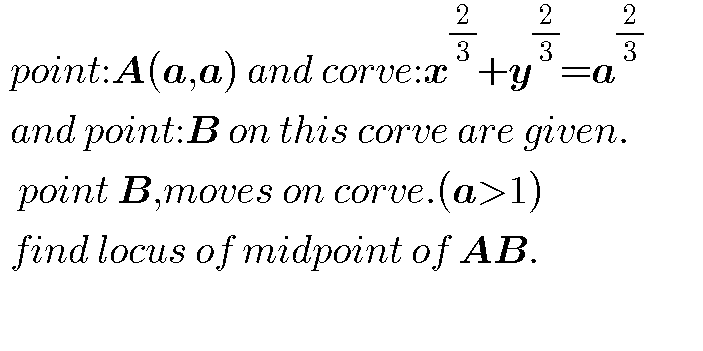
Question Number 40823 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 40822 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 40818 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40817 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40816 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 40815 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40814 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 40813 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 40804 Answers: 0 Comments: 6

Question Number 40787 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
Question Number 40786 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40782 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 40773 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40771 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
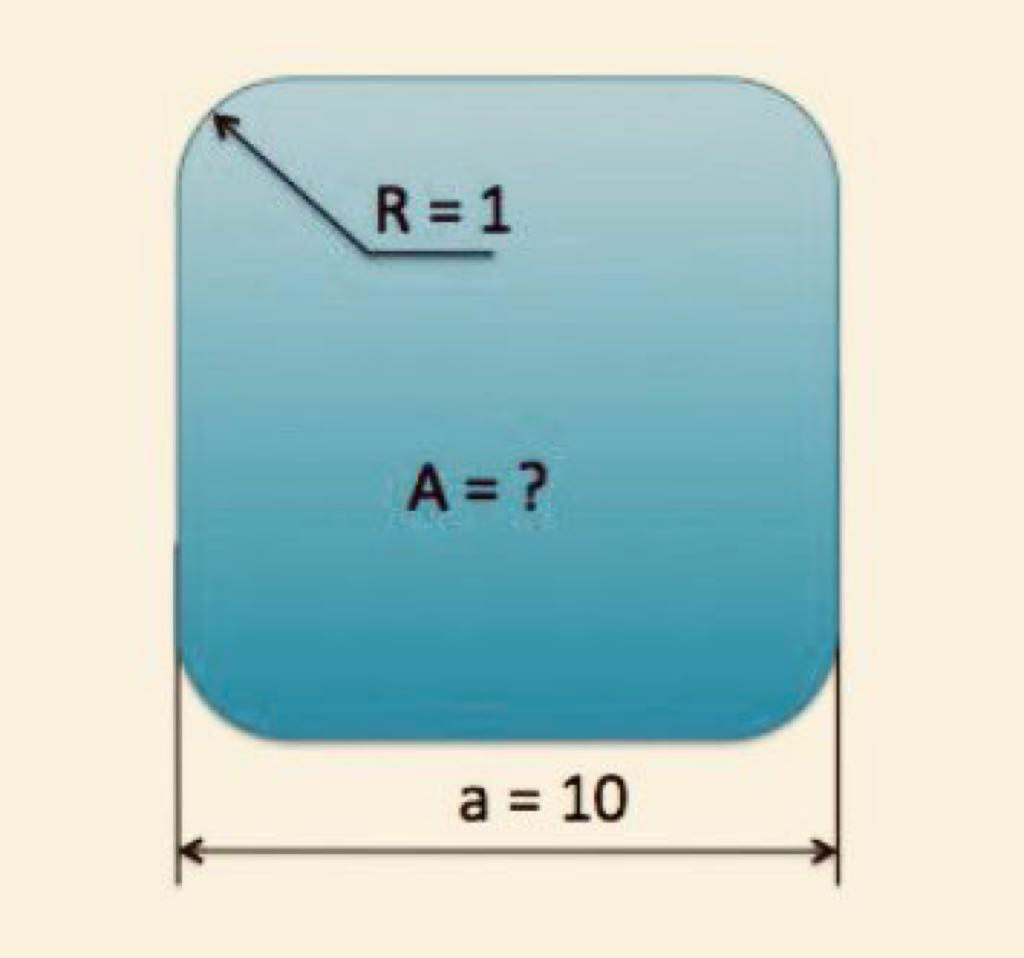
Question Number 40770 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40764 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 40763 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 40760 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 40759 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 40745 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
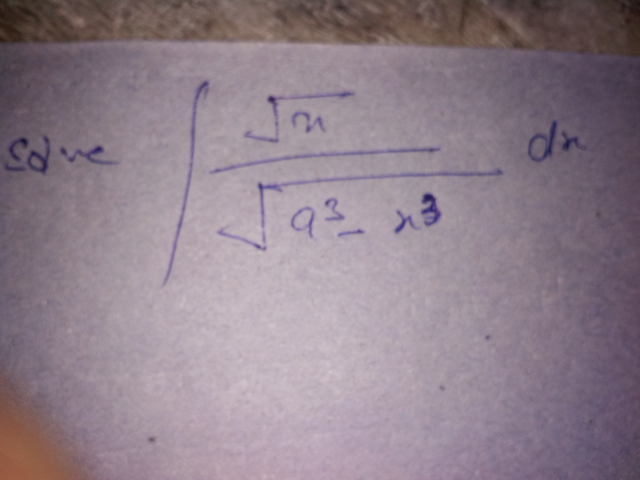
Question Number 40743 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 40740 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 40738 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Pg 1678 Pg 1679 Pg 1680 Pg 1681 Pg 1682 Pg 1683 Pg 1684 Pg 1685 Pg 1686 Pg 1687
