
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1676
Question Number 41454 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 41447 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 41444 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 41443 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 41479 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 41436 Answers: 4 Comments: 0

Question Number 41434 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
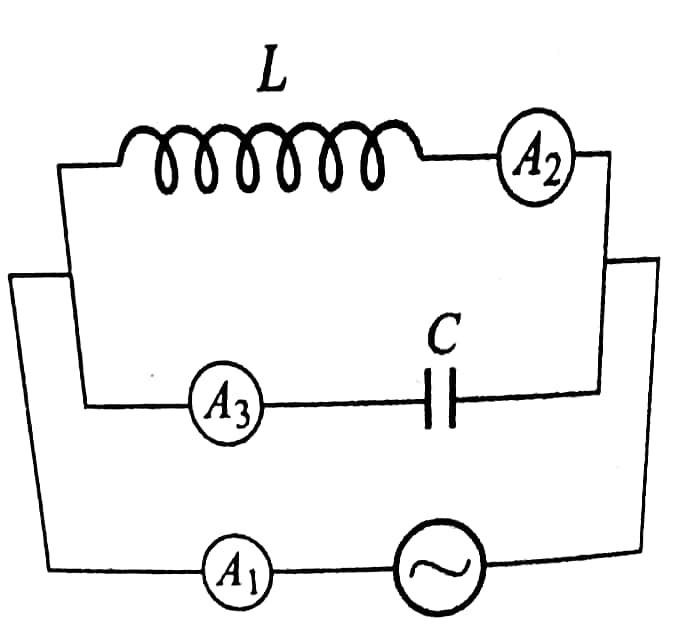
Question Number 41431 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 41410 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 41409 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 41408 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 41407 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 41394 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 41392 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 41390 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 41389 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 41388 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 41381 Answers: 2 Comments: 4

Question Number 41378 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 41371 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 41369 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
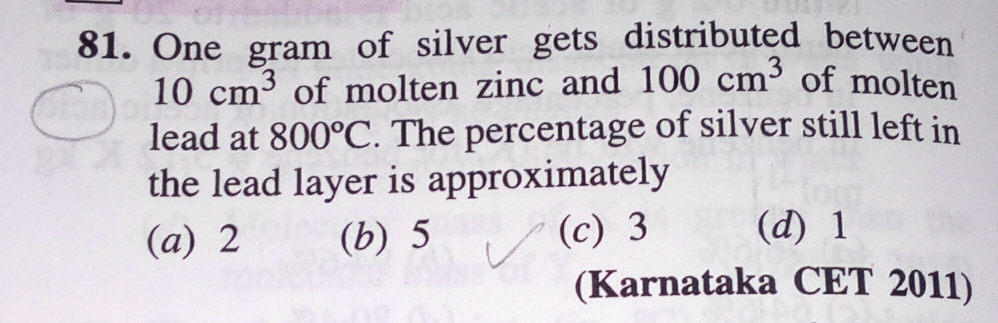
Question Number 41373 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 41349 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 41348 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 41347 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 41346 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
Pg 1671 Pg 1672 Pg 1673 Pg 1674 Pg 1675 Pg 1676 Pg 1677 Pg 1678 Pg 1679 Pg 1680
