
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1663
Question Number 42934 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
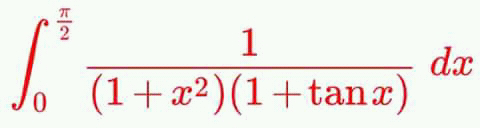
Question Number 42933 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 42910 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 42909 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 42908 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 42906 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 42897 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
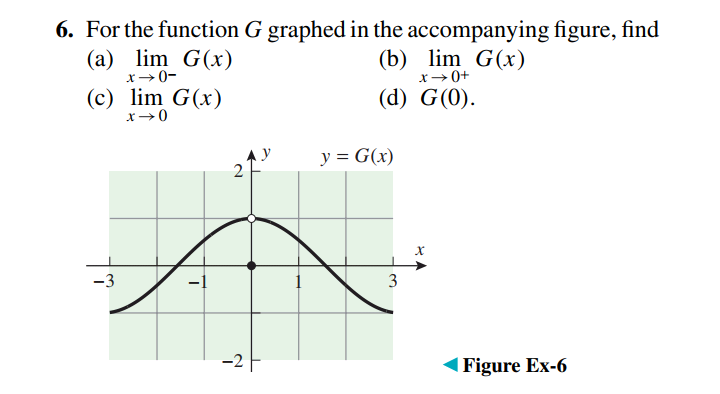
Question Number 42895 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
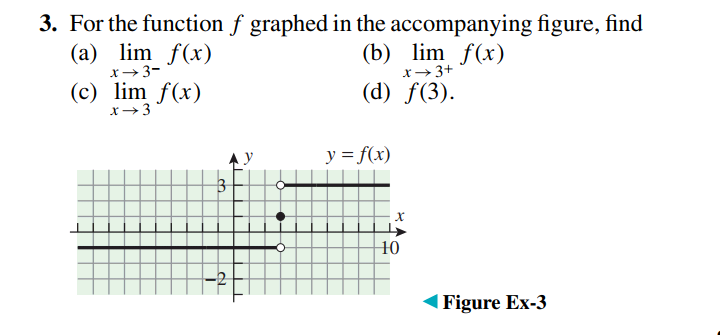
Question Number 42878 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
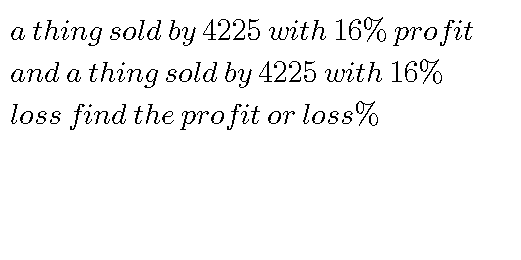
Question Number 42870 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 42866 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 42863 Answers: 2 Comments: 7

Question Number 42861 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{14}\boldsymbol{\div}\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{4}\right)=? \\ $$
Question Number 42826 Answers: 0 Comments: 7
Question Number 42823 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 42812 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 42810 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 42809 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 42808 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 42806 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 42805 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 42804 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 42803 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 42802 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 42801 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 42800 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\int\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\:{cosx}}{dx} \\ $$
Pg 1658 Pg 1659 Pg 1660 Pg 1661 Pg 1662 Pg 1663 Pg 1664 Pg 1665 Pg 1666 Pg 1667
