
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1659
Question Number 43489 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 43488 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 43486 Answers: 3 Comments: 1

Question Number 43481 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{i}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }{\left(\mathrm{3}+{i}\right)}= \\ $$
Question Number 43471 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 43470 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 43467 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 43465 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 43463 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 43461 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 43454 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 43452 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 43449 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
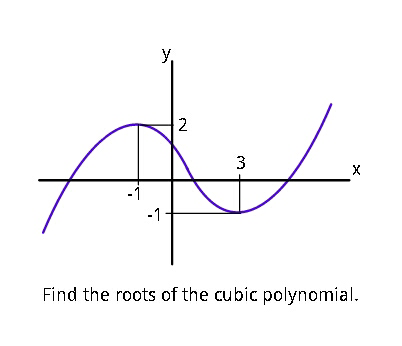
Question Number 43446 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 43441 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
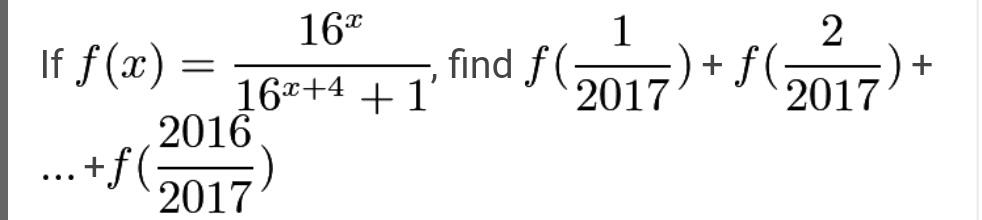
Question Number 43438 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 43434 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 43419 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
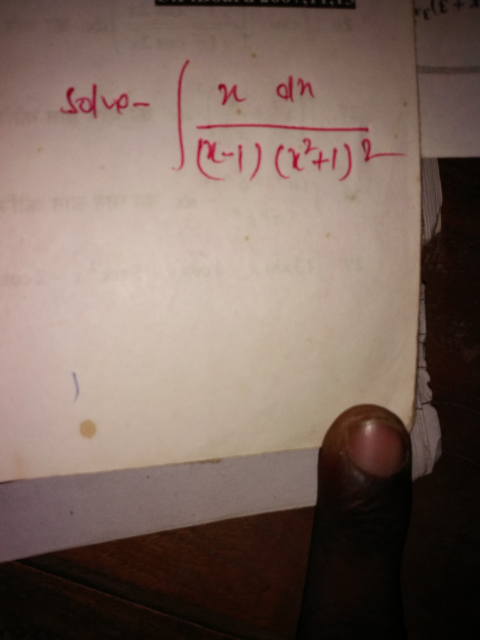
Question Number 43418 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 43417 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 43416 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 43404 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 43398 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 43395 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 43393 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 43391 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1654 Pg 1655 Pg 1656 Pg 1657 Pg 1658 Pg 1659 Pg 1660 Pg 1661 Pg 1662 Pg 1663
