
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1636
Question Number 46136 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 46121 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 46129 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 46110 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 46103 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 46101 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 46095 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 46091 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 46088 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 46087 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 46085 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
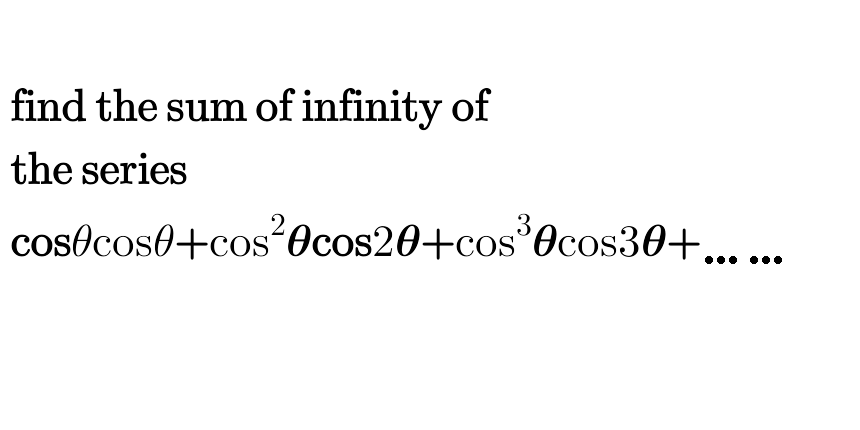
Question Number 46084 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 46083 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 46060 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 46045 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 46042 Answers: 4 Comments: 10

Question Number 46040 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 46073 Answers: 3 Comments: 1

Question Number 46032 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 46029 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 46025 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 46020 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 46014 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
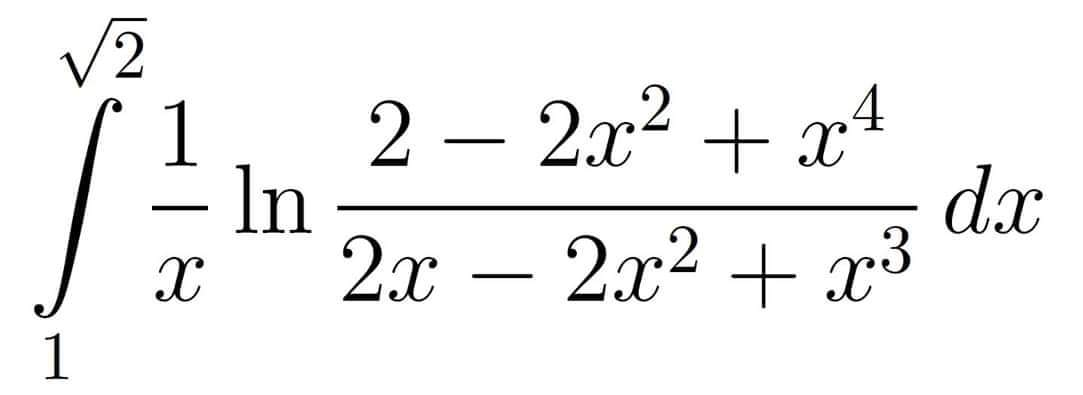
Question Number 46012 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 46011 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 46024 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 1631 Pg 1632 Pg 1633 Pg 1634 Pg 1635 Pg 1636 Pg 1637 Pg 1638 Pg 1639 Pg 1640
