
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1614
Question Number 48668 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 48667 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 48664 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 48659 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 48656 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 48653 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 48643 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 48638 Answers: 1 Comments: 4

Question Number 48616 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 48611 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 48610 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 48585 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 48581 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 48567 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
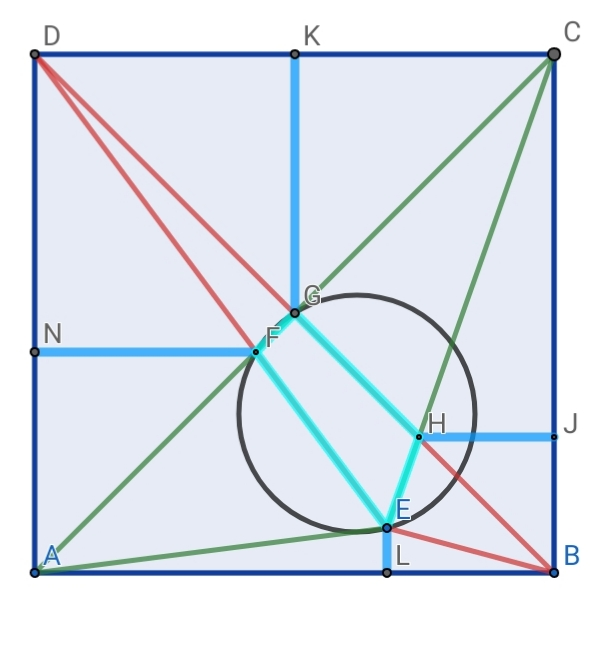
Question Number 48560 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
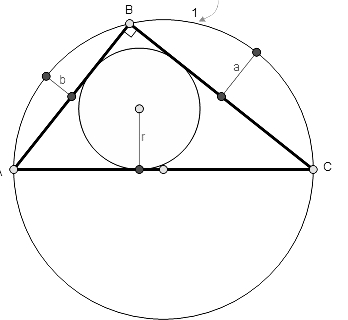
Question Number 48559 Answers: 3 Comments: 0

Question Number 48553 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 48543 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 48541 Answers: 1 Comments: 12

Question Number 48540 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
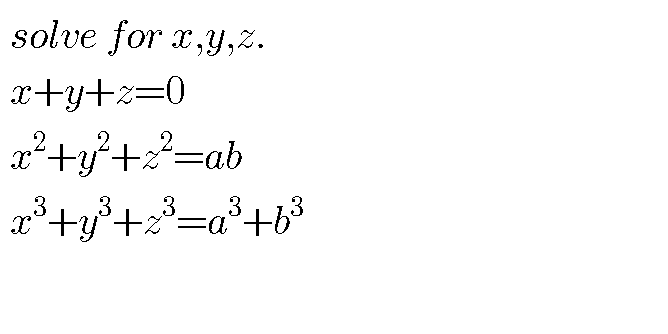
Question Number 48529 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 48528 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 48527 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 48526 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 48525 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 48524 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 1609 Pg 1610 Pg 1611 Pg 1612 Pg 1613 Pg 1614 Pg 1615 Pg 1616 Pg 1617 Pg 1618
