
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1610
Question Number 49111 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 49101 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49100 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49099 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49097 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 49096 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 49095 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 49094 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 49093 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 49092 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49090 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 49083 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49078 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
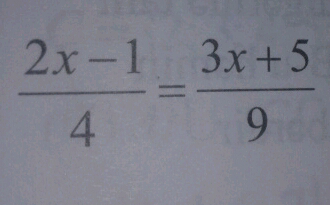
Question Number 49077 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49064 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 49061 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 49060 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
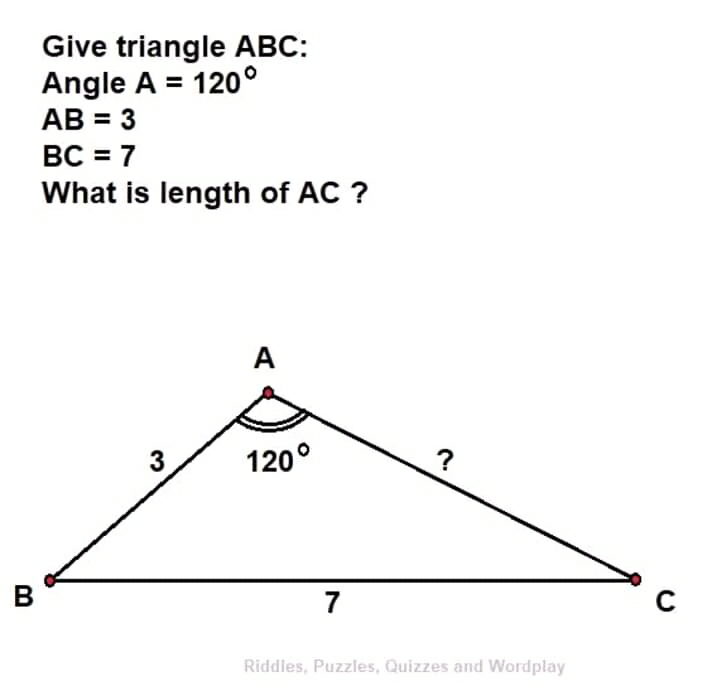
Question Number 49037 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49036 Answers: 1 Comments: 4

Question Number 49035 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 49034 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 49032 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{dx}=?? \\ $$
Question Number 49028 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 49020 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
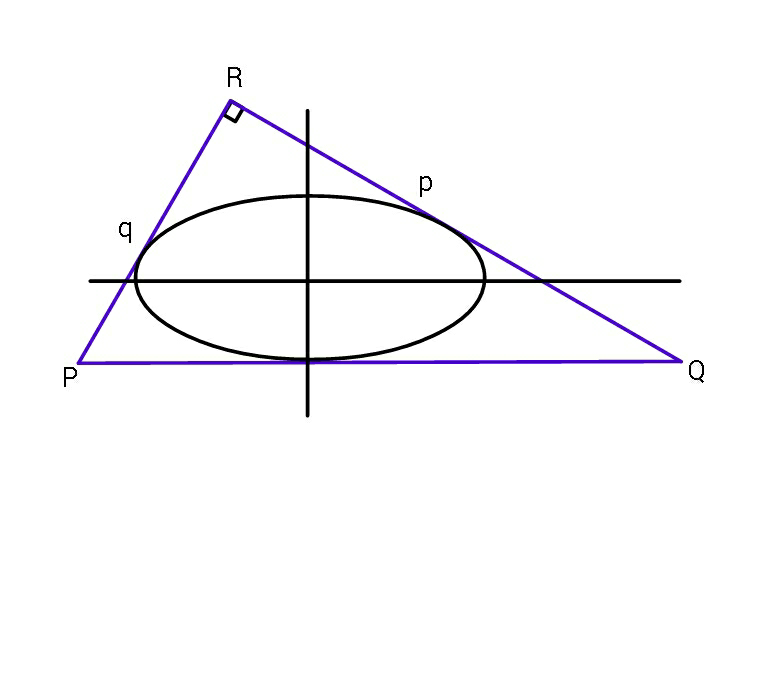
Question Number 49008 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
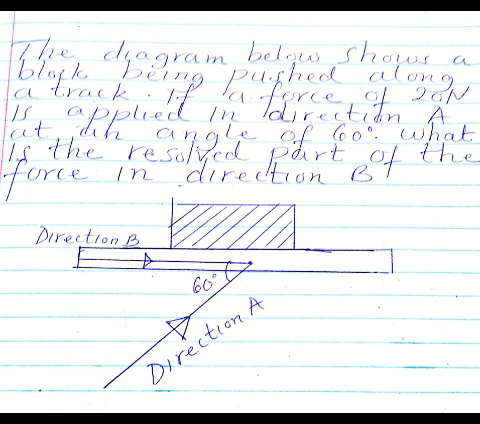
Question Number 49007 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Pg 1605 Pg 1606 Pg 1607 Pg 1608 Pg 1609 Pg 1610 Pg 1611 Pg 1612 Pg 1613 Pg 1614
