
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1589
Question Number 51588 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 51605 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 51571 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 51558 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 51552 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 51551 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 51550 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$${find}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 51549 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 51539 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
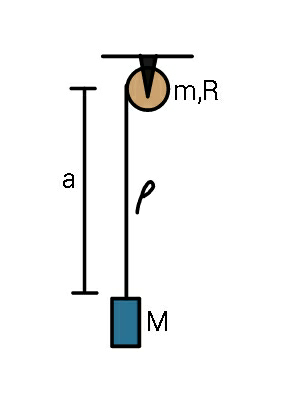
Question Number 51535 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 51526 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 51510 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
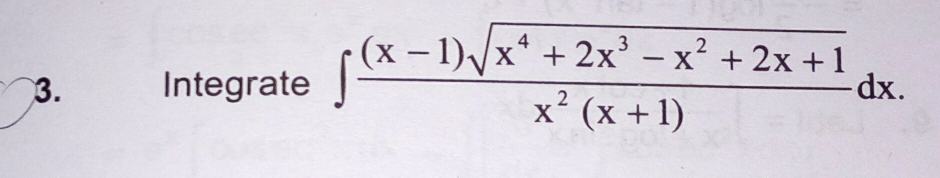
Question Number 51508 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 51502 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 51501 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 51507 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 51494 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 51492 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 51489 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 51485 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 51520 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 51448 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 51446 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 51436 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 51431 Answers: 3 Comments: 3
Question Number 51466 Answers: 1 Comments: 5
Pg 1584 Pg 1585 Pg 1586 Pg 1587 Pg 1588 Pg 1589 Pg 1590 Pg 1591 Pg 1592 Pg 1593
