
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1583
Question Number 52349 Answers: 2 Comments: 3
Question Number 52341 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 52340 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 52324 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 52321 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
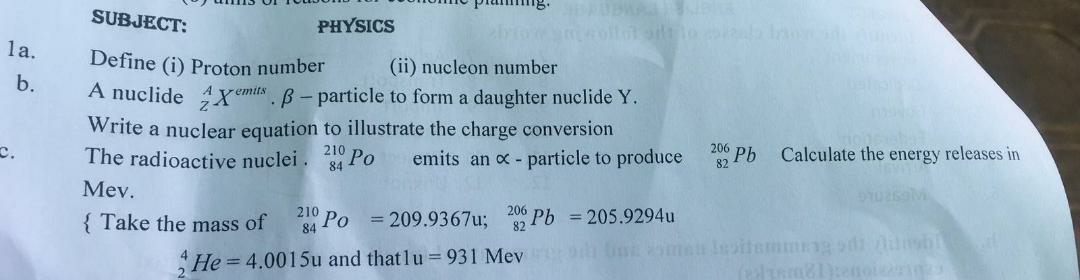
Question Number 52305 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 52299 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 52312 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
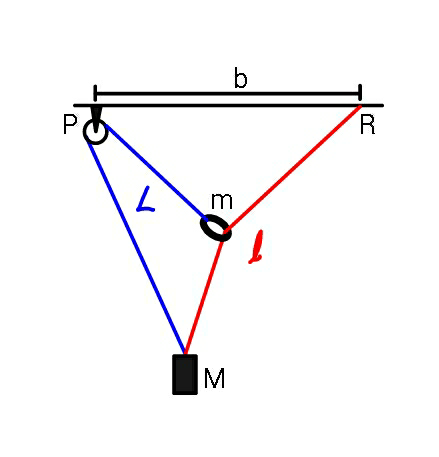
Question Number 52282 Answers: 1 Comments: 7
Question Number 52278 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 52275 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 52276 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 52273 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 52268 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 52261 Answers: 0 Comments: 9
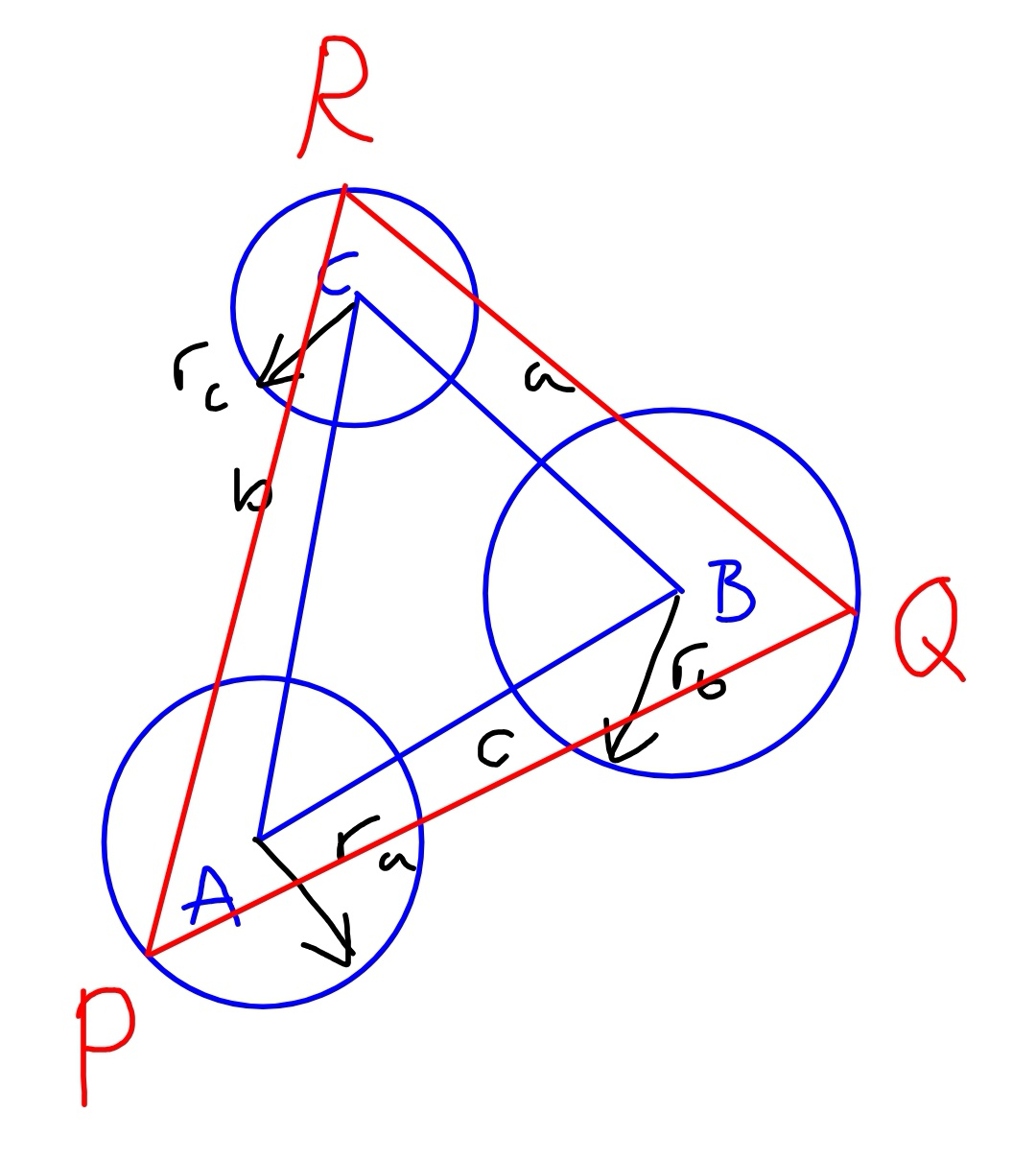
Question Number 52258 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 52240 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 52233 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 52223 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 52222 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 52221 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 52206 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 52208 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 52214 Answers: 2 Comments: 4

Question Number 52200 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 52198 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Pg 1578 Pg 1579 Pg 1580 Pg 1581 Pg 1582 Pg 1583 Pg 1584 Pg 1585 Pg 1586 Pg 1587
