
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1570
Question Number 54160 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 54156 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 54152 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 54137 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 54126 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54116 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
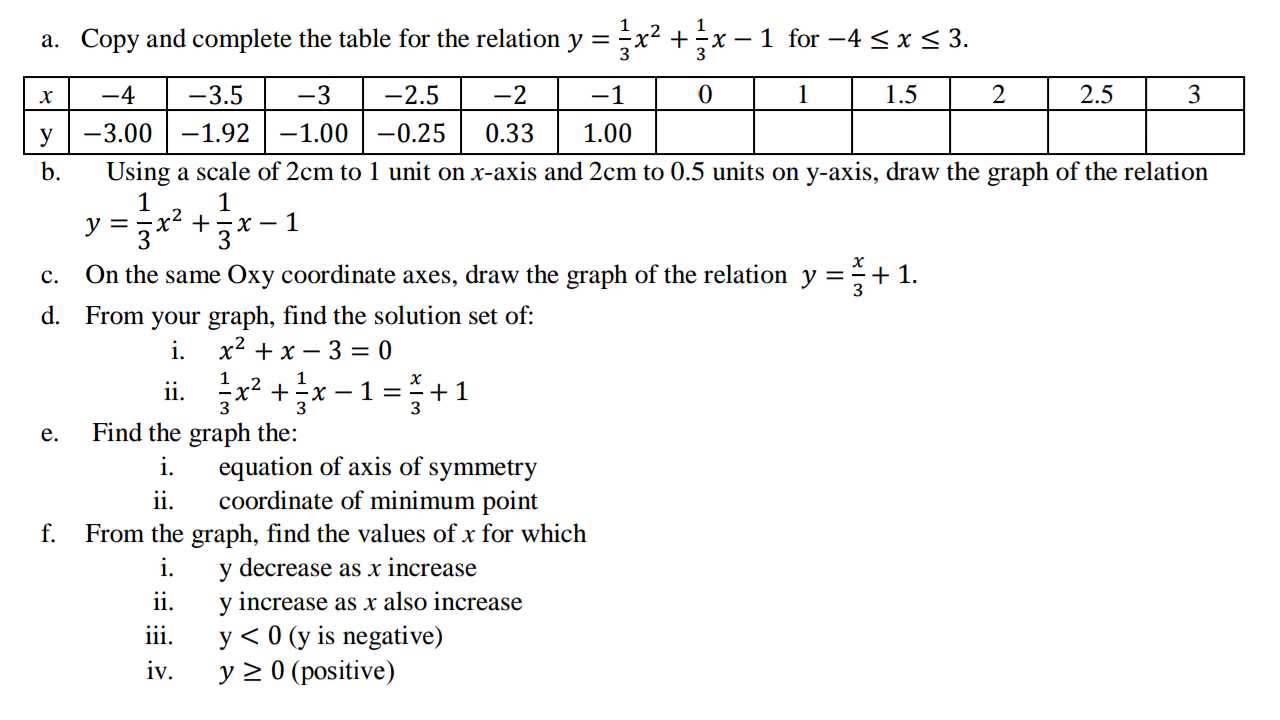
Question Number 54102 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 54093 Answers: 0 Comments: 8
Question Number 54074 Answers: 1 Comments: 5
Question Number 54073 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 54070 Answers: 2 Comments: 7
Question Number 54068 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 54061 Answers: 0 Comments: 8
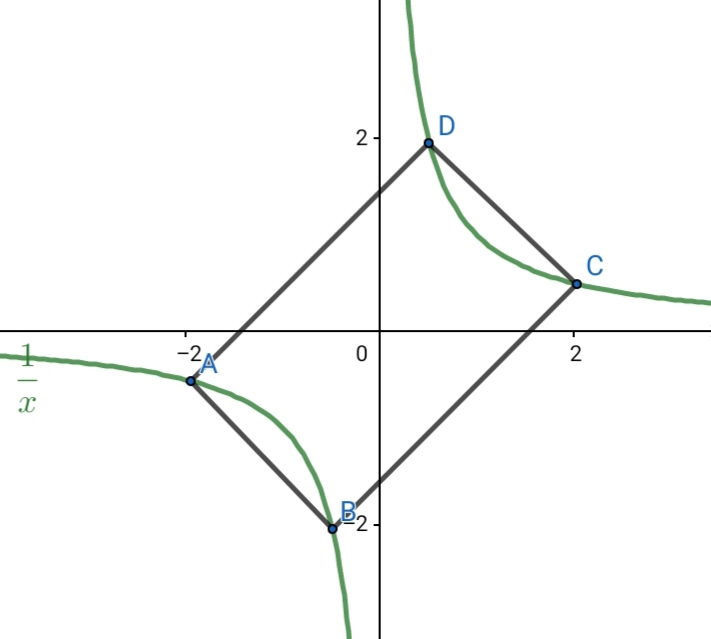
Question Number 54051 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
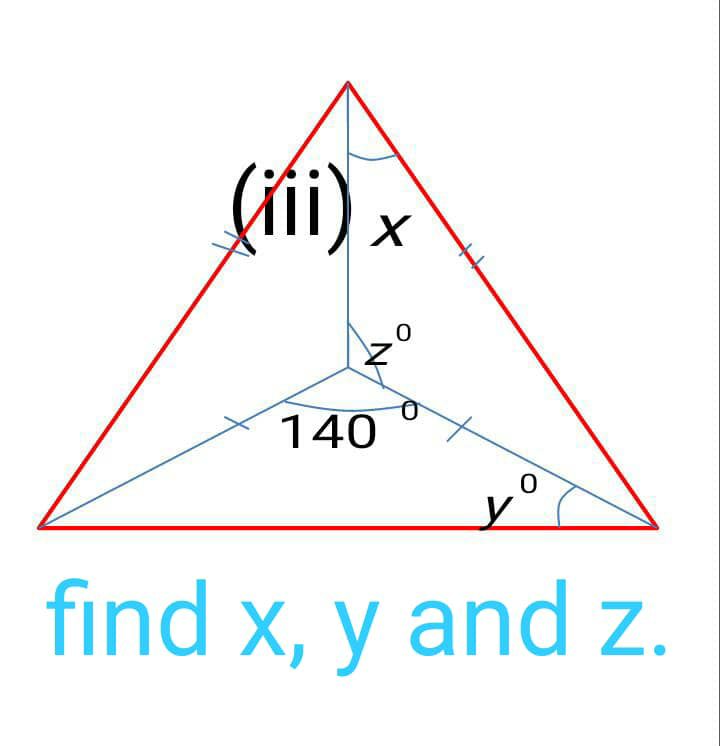
Question Number 54045 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 54034 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 54033 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 54032 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 54031 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54029 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54028 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54025 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54024 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54022 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 54015 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54013 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1565 Pg 1566 Pg 1567 Pg 1568 Pg 1569 Pg 1570 Pg 1571 Pg 1572 Pg 1573 Pg 1574
