
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1565
Question Number 54788 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 54787 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 54786 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 54777 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 54775 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 54770 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 54767 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54765 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 54756 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54755 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 54745 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 54741 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54740 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 54737 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 54730 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 54716 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
Question Number 54721 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 54701 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
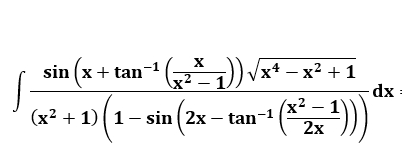
Question Number 54700 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54699 Answers: 2 Comments: 3
Question Number 54698 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 54679 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 54675 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54688 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 54663 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$${y}\:=\:{cos}\mathrm{2}{t}×{sen}\mathrm{2}{t} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${y}'\:=\:? \\ $$
Question Number 54661 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Pg 1560 Pg 1561 Pg 1562 Pg 1563 Pg 1564 Pg 1565 Pg 1566 Pg 1567 Pg 1568 Pg 1569
