
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1529
Question Number 58756 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
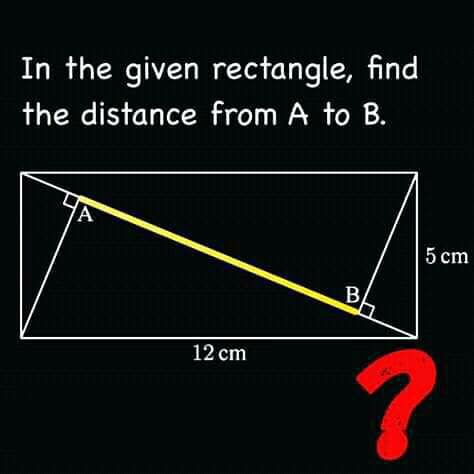
Question Number 58754 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
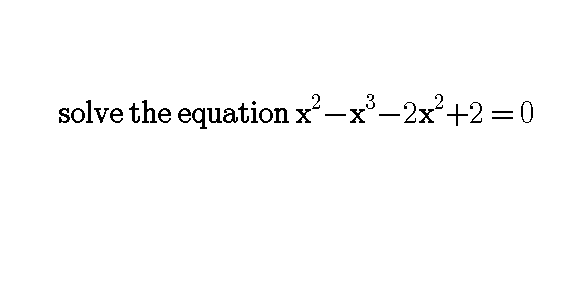
Question Number 58753 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 58750 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 58720 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:{given}\:{that}\:\:{y}\:=\:{cos}\left({x}°\right) \\ $$
Question Number 58717 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 58716 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Question Number 58700 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 58698 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
Question Number 58696 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
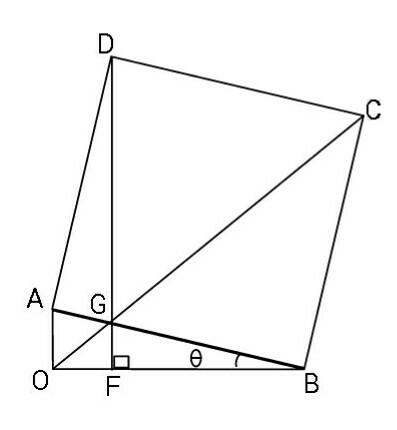
Question Number 58686 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 58682 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{3}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{2}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{15}} \\ $$
Question Number 58675 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 58671 Answers: 3 Comments: 2
Question Number 58669 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 58668 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 58663 Answers: 3 Comments: 0

Question Number 58660 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 58652 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 58648 Answers: 2 Comments: 4

Question Number 58644 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 58641 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\mathrm{What}\:\mathrm{is}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}? \\ $$
Question Number 58639 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 58627 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 58626 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 58622 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Pg 1524 Pg 1525 Pg 1526 Pg 1527 Pg 1528 Pg 1529 Pg 1530 Pg 1531 Pg 1532 Pg 1533
