
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1485
Question Number 62340 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
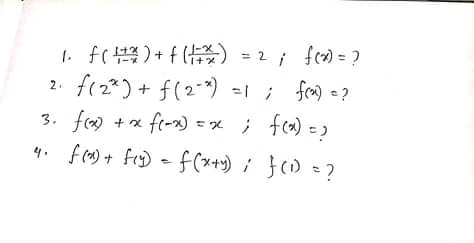
Question Number 62338 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
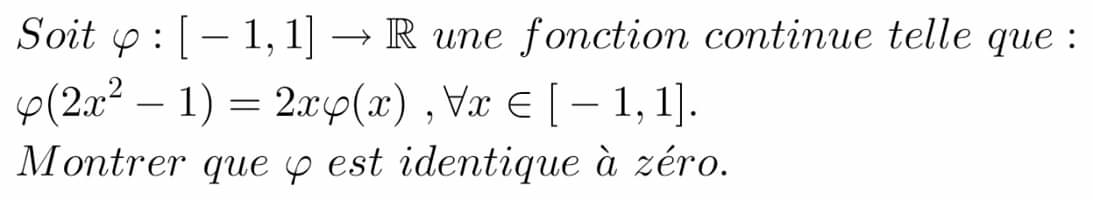
Question Number 62335 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 62334 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 62332 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
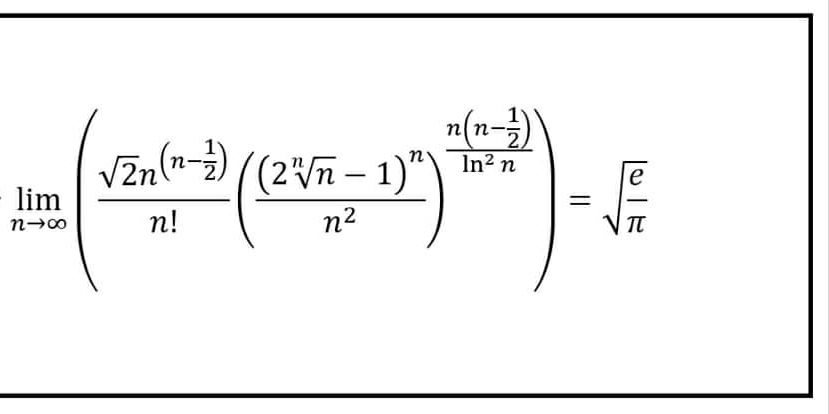
Question Number 62330 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 62322 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
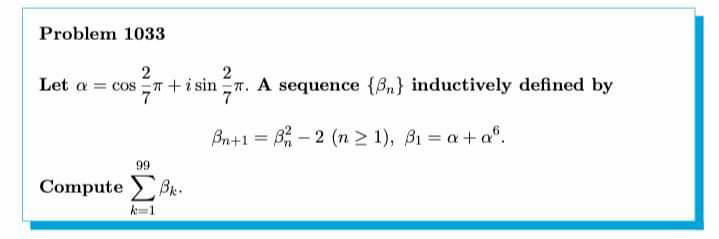
Question Number 62308 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 62291 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 62288 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 62289 Answers: 3 Comments: 0

Question Number 62281 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 62276 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 62275 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 62274 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 62273 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 62266 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 62265 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 62263 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 62262 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 62252 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 62251 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 62244 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 62242 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 62234 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 62232 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Pg 1480 Pg 1481 Pg 1482 Pg 1483 Pg 1484 Pg 1485 Pg 1486 Pg 1487 Pg 1488 Pg 1489
