
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1469
Question Number 65200 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
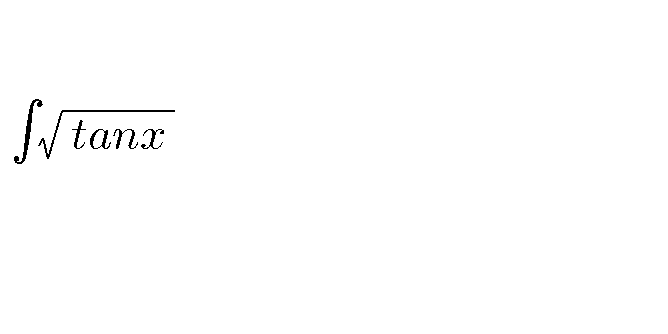
Question Number 65199 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 65198 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 65196 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65195 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65194 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65193 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 65192 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65189 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65170 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65168 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 65166 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 65162 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 65153 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 65148 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 65137 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 65134 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 65133 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 65132 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65131 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 65130 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 65129 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 65128 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 65122 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 65119 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 65102 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Pg 1464 Pg 1465 Pg 1466 Pg 1467 Pg 1468 Pg 1469 Pg 1470 Pg 1471 Pg 1472 Pg 1473
