
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1459
Question Number 66005 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${solve}\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{''} \:+{xy}^{'} −\mathrm{3}{y}\:=\mathrm{4}{e}^{−{x}} \\ $$
Question Number 66004 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65992 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 65988 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
Question Number 66041 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 65983 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 65972 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65971 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 65970 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65961 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65951 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 65950 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi/\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{tan}\:^{\mathrm{3}} {xdx}\:=\:? \\ $$
Question Number 68063 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 65981 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 65980 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
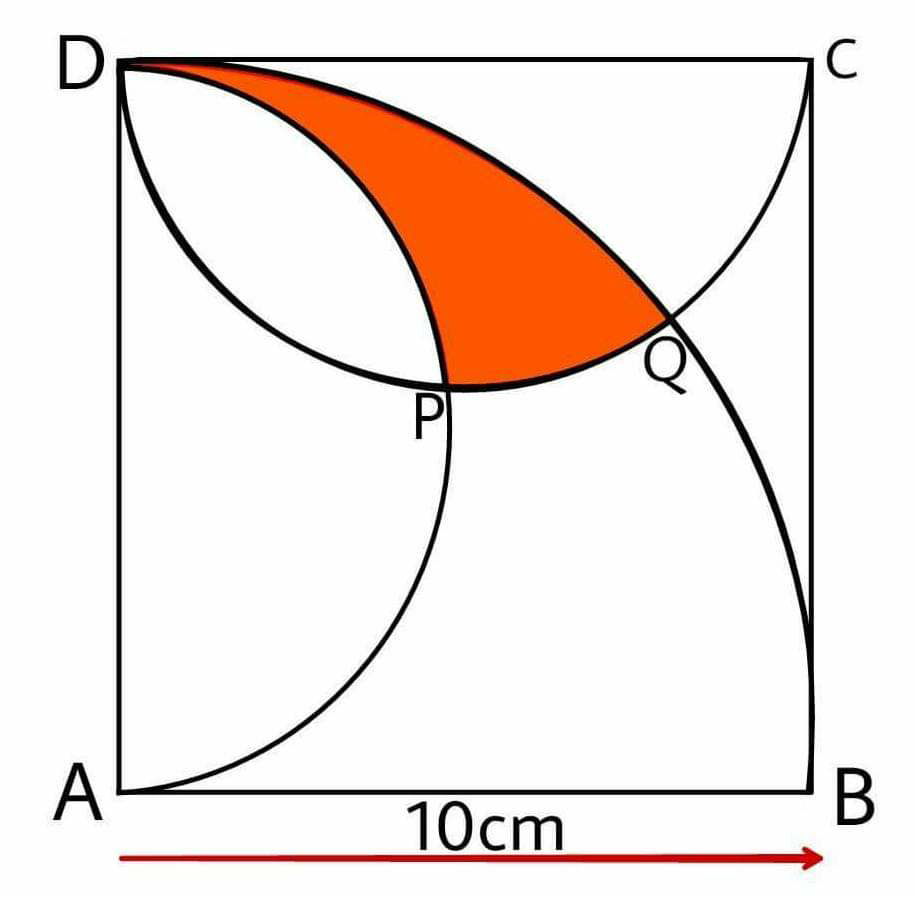
Question Number 65945 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 65959 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65934 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 65931 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65930 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 65929 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 65926 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65925 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 65924 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 65923 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 65922 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 1454 Pg 1455 Pg 1456 Pg 1457 Pg 1458 Pg 1459 Pg 1460 Pg 1461 Pg 1462 Pg 1463
