
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1457
Question Number 66342 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66341 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66340 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66339 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66338 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66337 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66336 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66335 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66334 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66332 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66330 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66328 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66326 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 66324 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66323 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66322 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66321 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66319 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66318 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 66317 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66316 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 66325 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 66308 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66310 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
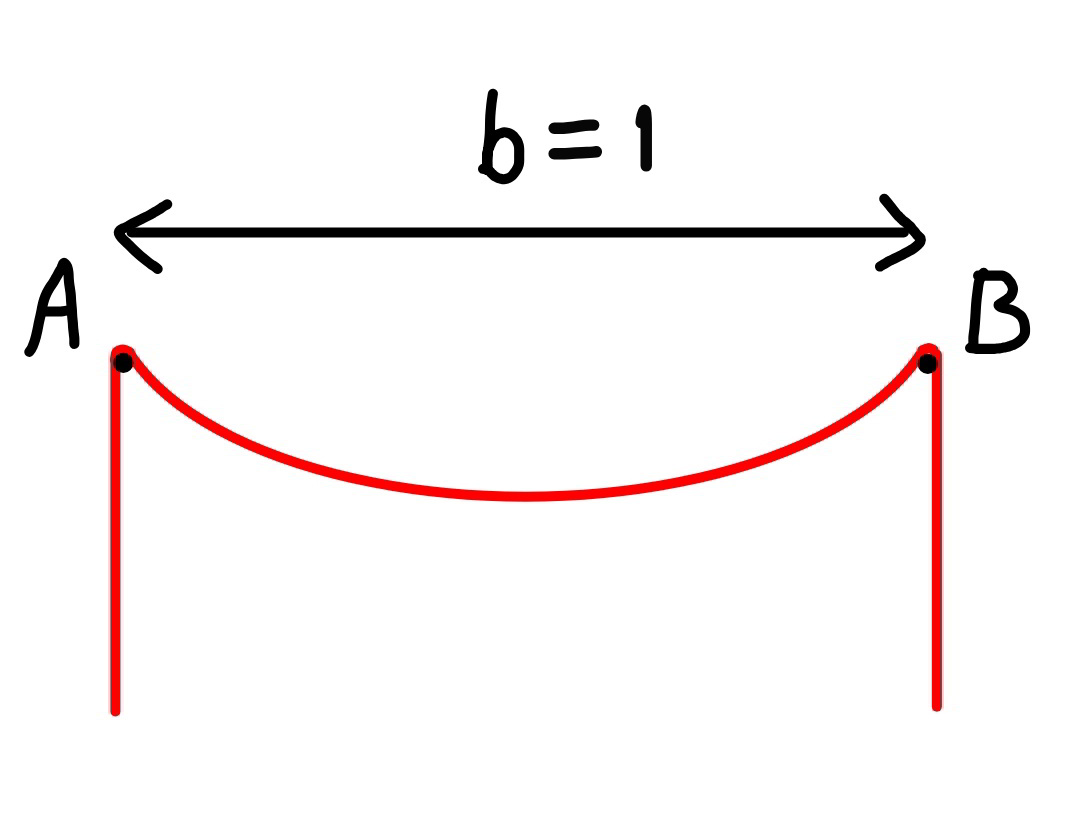
Question Number 66309 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66304 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1452 Pg 1453 Pg 1454 Pg 1455 Pg 1456 Pg 1457 Pg 1458 Pg 1459 Pg 1460 Pg 1461
