
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1456
Question Number 66421 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 66420 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 66418 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66406 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 66405 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 66404 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 66403 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 66401 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 66399 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66396 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 66413 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 66412 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 66382 Answers: 0 Comments: 14
Question Number 66379 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
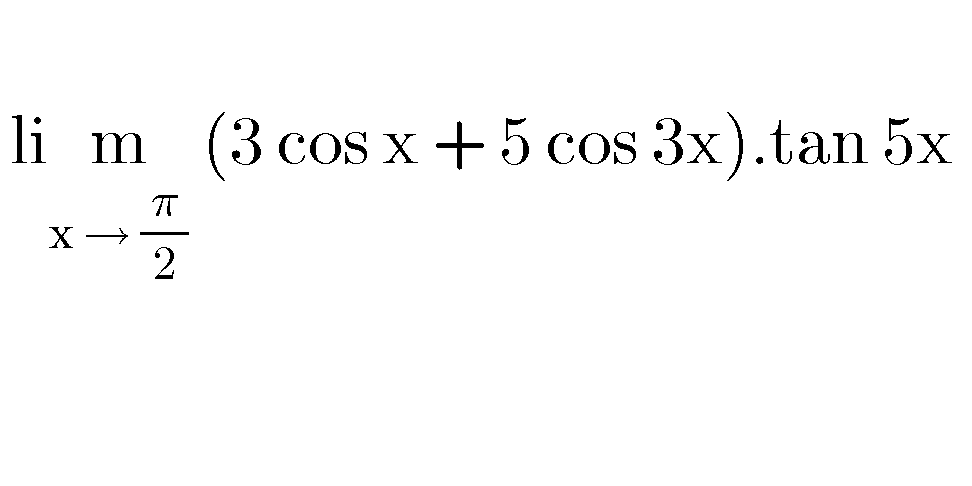
Question Number 66381 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
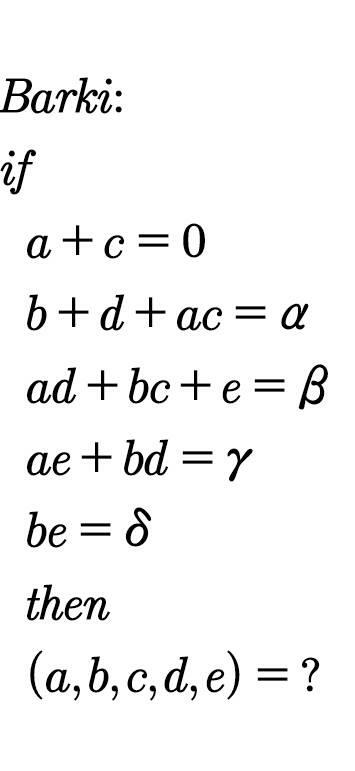
Question Number 66356 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 66355 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66354 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66351 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66350 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66349 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66348 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:{nature}\:{of}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{{e}^{{x}} −{cosx}} \\ $$
Question Number 66347 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66346 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66345 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66344 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 1451 Pg 1452 Pg 1453 Pg 1454 Pg 1455 Pg 1456 Pg 1457 Pg 1458 Pg 1459 Pg 1460
