
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1455
Question Number 66508 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
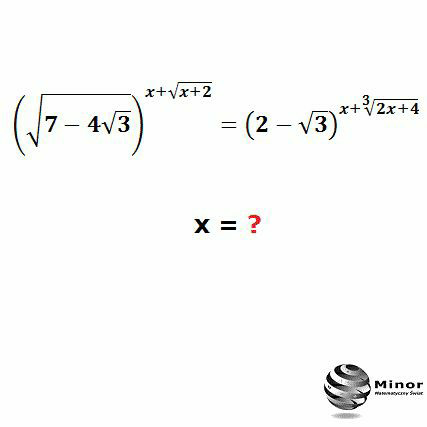
Question Number 66502 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${find}\:{the}\:{area}\:{about}\:{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}\theta\right) \\ $$
Question Number 66498 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 66497 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 66489 Answers: 3 Comments: 0

Question Number 66483 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 66478 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66476 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 66474 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66472 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 66470 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 66469 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 66468 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66467 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66466 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66465 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66464 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66681 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 66462 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66461 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 66459 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66446 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66444 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 66439 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 66434 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 66433 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 1450 Pg 1451 Pg 1452 Pg 1453 Pg 1454 Pg 1455 Pg 1456 Pg 1457 Pg 1458 Pg 1459
