
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1440
Question Number 68150 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 68149 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 68145 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 68133 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 68132 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 68129 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 68141 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 68122 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 68116 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{{sin}\mathrm{2}{x}−{sec}\left({x}\right)} \\ $$
Question Number 68113 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{Solve} \\ $$$${y}.{y}''\:=\:\mathrm{3}\left({y}'\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Question Number 68110 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 68100 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 68096 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 68095 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\sqrt{{x}}/\mathrm{1}+\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{{x}\:}\:{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 68094 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int{dx}/\sqrt[{{x}}]{\left(\pi+{e}\right)^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }\: \\ $$
Question Number 68092 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
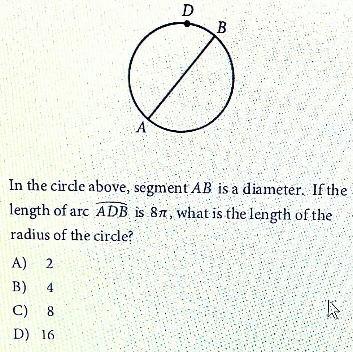
Question Number 68087 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 68079 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 68078 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 68077 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 68073 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 68068 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 68062 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
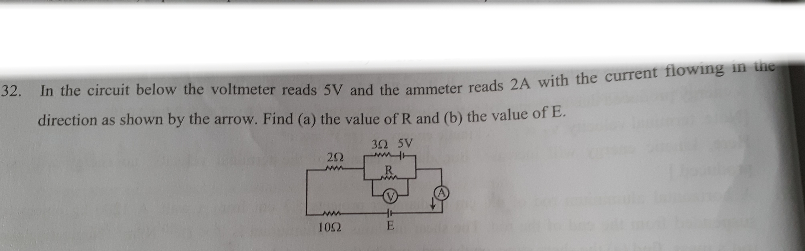
Question Number 68052 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
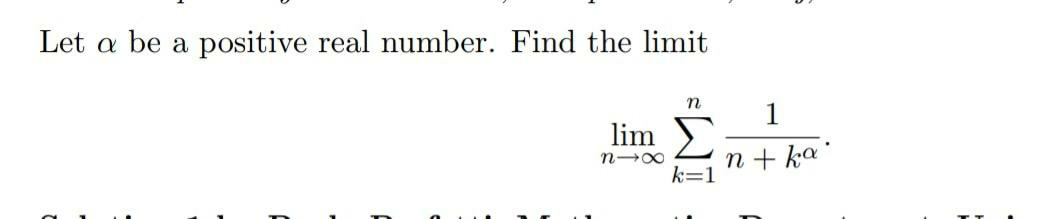
Question Number 68046 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 68041 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Pg 1435 Pg 1436 Pg 1437 Pg 1438 Pg 1439 Pg 1440 Pg 1441 Pg 1442 Pg 1443 Pg 1444
