
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1428
Question Number 69393 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 69390 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 69389 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\int_{\mid{z}+{i}\mid=\mathrm{3}} \:\:\frac{{sinz}}{{z}+{i}}{dz} \\ $$
Question Number 69379 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 69377 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 69376 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 69375 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 69374 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 69373 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 69585 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
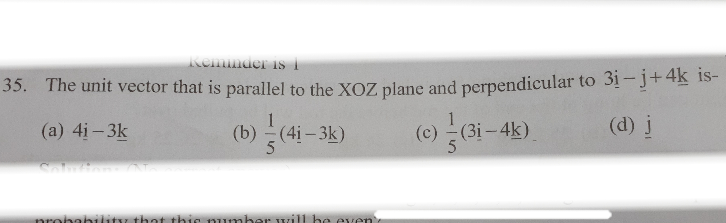
Question Number 69355 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 69347 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 69338 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 69412 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 69411 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 69328 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 69482 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}+{cosn}}{\mathrm{4}{n}+{sinn}}\:=\:? \\ $$
Question Number 74637 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 69319 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 69385 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 69327 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 69293 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 69297 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 69296 Answers: 0 Comments: 6

Question Number 69314 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$${if}\:\mathrm{5}\:{x}\:{y}\:\mathrm{40}\:{are}\:{in}\:{GP}\:.{find}\:{x}\:{and}\:{y} \\ $$
Question Number 69272 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
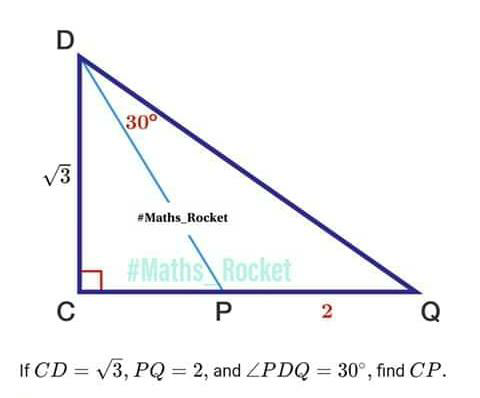
Pg 1423 Pg 1424 Pg 1425 Pg 1426 Pg 1427 Pg 1428 Pg 1429 Pg 1430 Pg 1431 Pg 1432
