
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1415
Question Number 71593 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
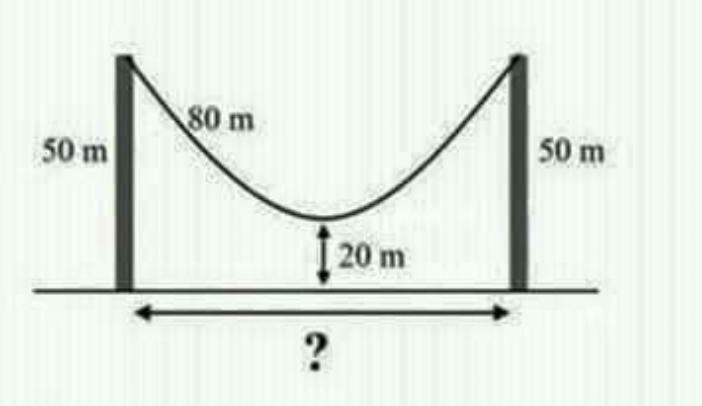
Question Number 71578 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 71572 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 71570 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 71564 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$$\left(\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{i}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} =−\mathrm{7}+\mathrm{24i} \\ $$
Question Number 71563 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 71560 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 71551 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${whats}\:{the}\:{mean}\:{R}^{++} \:?{and}\:{R}^{−−} ? \\ $$
Question Number 71550 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
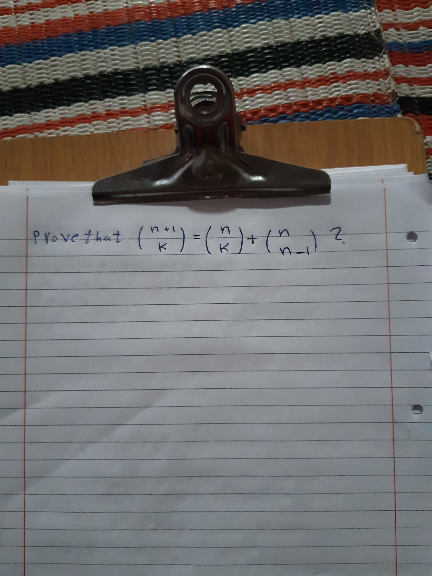
Question Number 71548 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 71538 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 71534 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 71533 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 71518 Answers: 1 Comments: 8
$$\mathrm{Express}\:\:\sqrt{\mathrm{28}}\:\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{continued}\:\mathrm{fraction} \\ $$
Question Number 71517 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
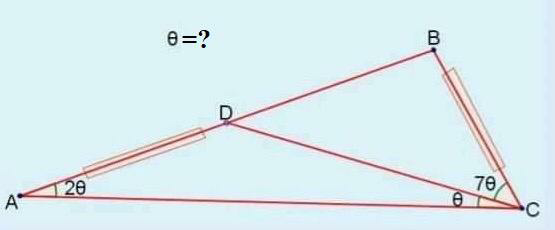
Question Number 71516 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 71508 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 71499 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 71490 Answers: 2 Comments: 2

Question Number 71506 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 71513 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
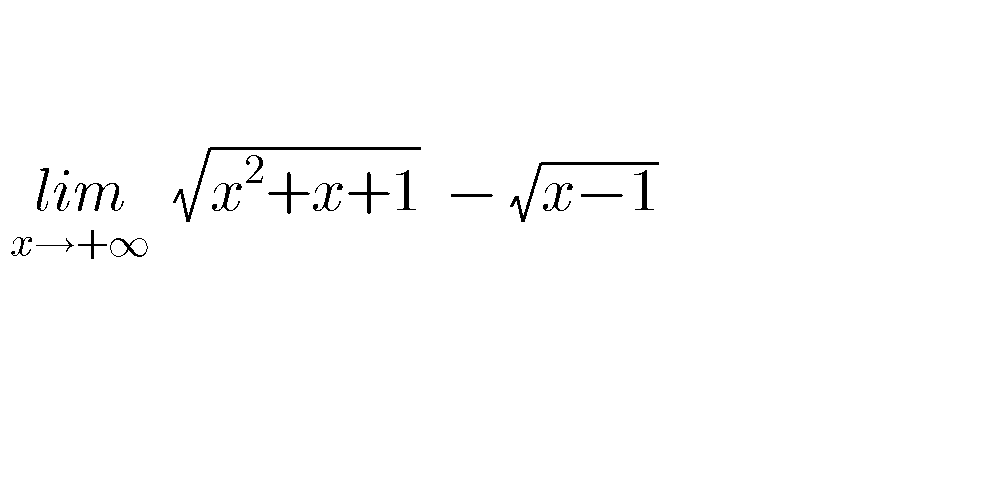
Question Number 71448 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 71673 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 71439 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 71432 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 71423 Answers: 0 Comments: 7

Pg 1410 Pg 1411 Pg 1412 Pg 1413 Pg 1414 Pg 1415 Pg 1416 Pg 1417 Pg 1418 Pg 1419
