
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1414
Question Number 67187 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 67167 Answers: 4 Comments: 2
Question Number 67153 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 67148 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
Question Number 67138 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${find}\:{the}\:{area}\:{abounded}\:{y}=\sqrt{{x}} \\ $$$${and}\:{y}={x}−\mathrm{2}? \\ $$
Question Number 67136 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 67122 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 67116 Answers: 4 Comments: 1

Question Number 67108 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 67106 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${find}\:{the}\:{area}\:{abounded}\:{y}=\sqrt{{x}} \\ $$$${afind}\:{y}={x}−\mathrm{2}? \\ $$
Question Number 67105 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:{the}\:{area}\:{abounded}\:{y}=\sqrt{{x}} \\ $$$${afind}\:{y}={x}−\mathrm{2}? \\ $$
Question Number 67102 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
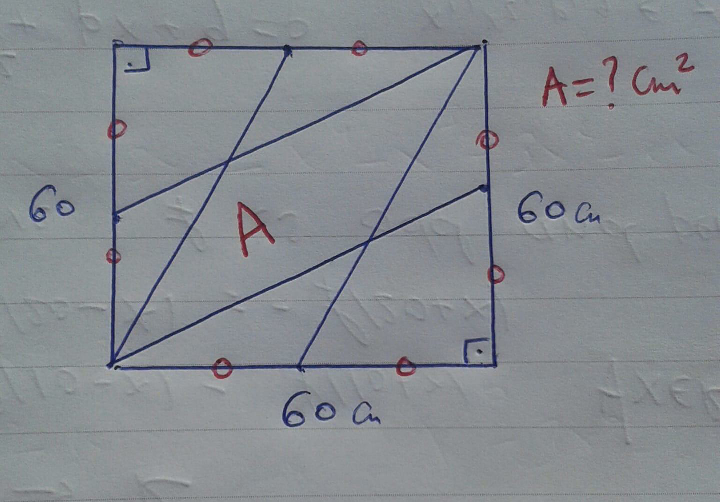
Question Number 67083 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 67072 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 67071 Answers: 0 Comments: 7

Question Number 67070 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 67069 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 67059 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 67058 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 67057 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 67055 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 67038 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 67035 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 67034 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
$${calculate}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{nx}\right)}{{n}} \\ $$
Question Number 67033 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 67032 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
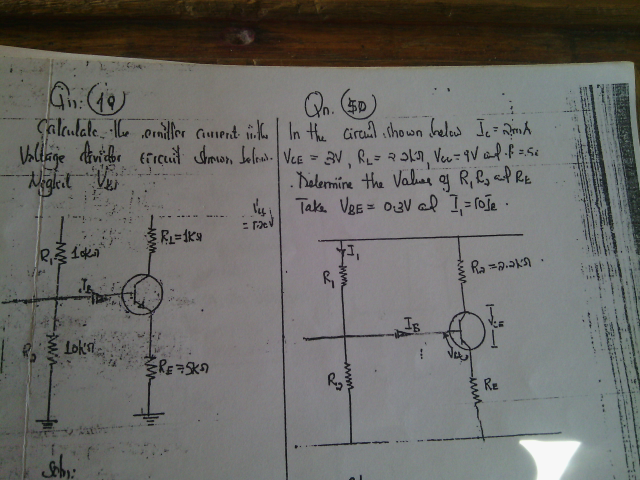
Pg 1409 Pg 1410 Pg 1411 Pg 1412 Pg 1413 Pg 1414 Pg 1415 Pg 1416 Pg 1417 Pg 1418
