
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1387
Question Number 74912 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 74904 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 74900 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 74910 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 74891 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 74890 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 74889 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 74888 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 74887 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 74886 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 74885 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${calcilate}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{16}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$
Question Number 74884 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 74882 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 74880 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 74870 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 74863 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 76203 Answers: 0 Comments: 7

Question Number 74861 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
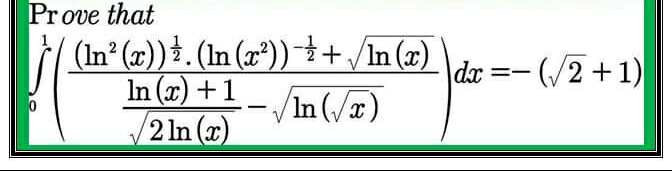
Question Number 74860 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
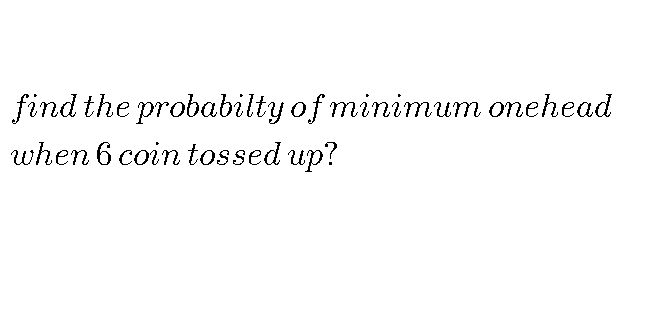
Question Number 74853 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 74840 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 74825 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
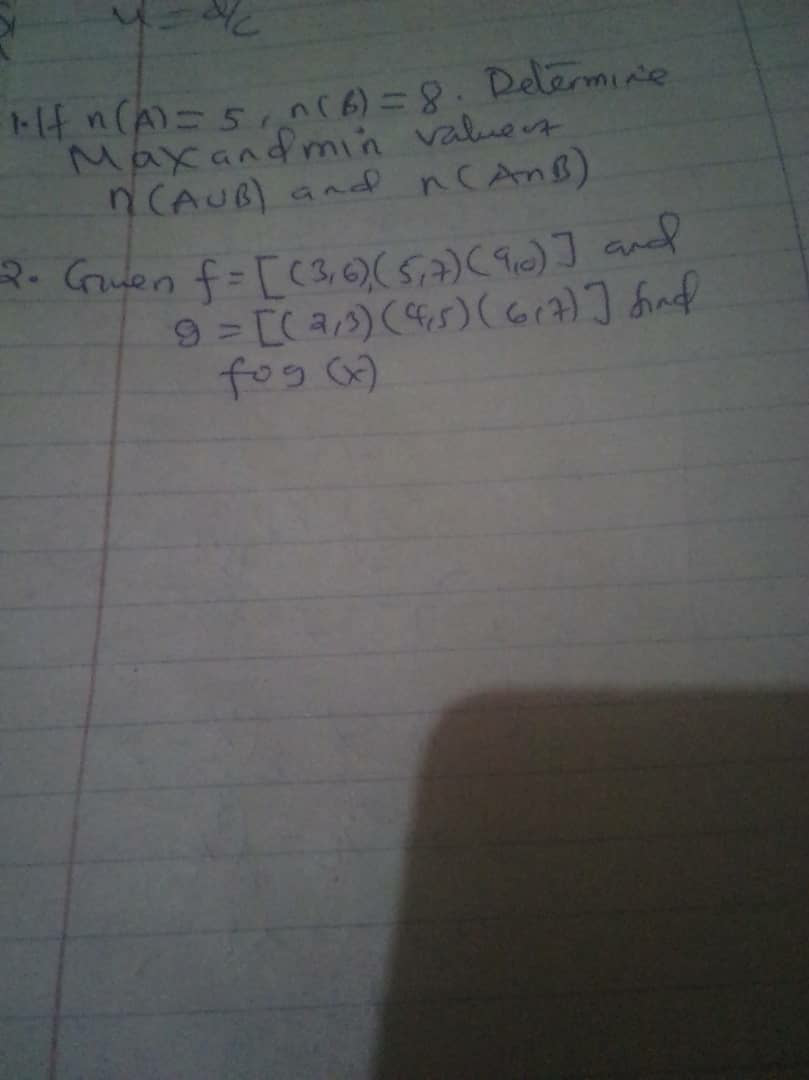
Question Number 74821 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
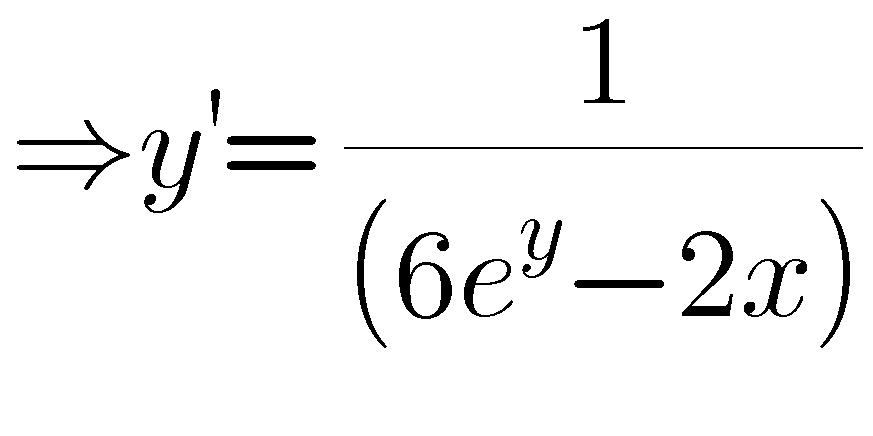
Question Number 74819 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 74817 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 74802 Answers: 1 Comments: 4

Pg 1382 Pg 1383 Pg 1384 Pg 1385 Pg 1386 Pg 1387 Pg 1388 Pg 1389 Pg 1390 Pg 1391
