
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1384
Question Number 75272 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75268 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75267 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 75260 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75259 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75255 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
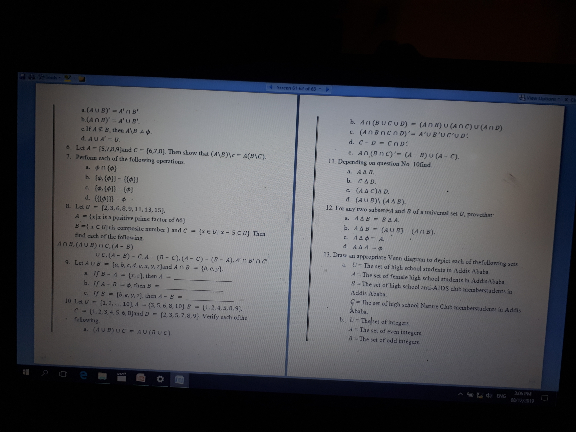
Question Number 75254 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
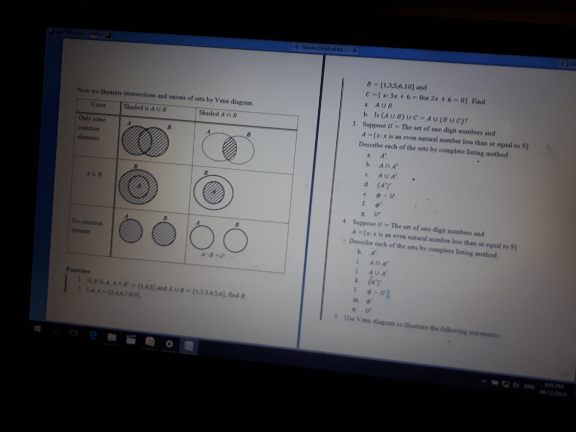
Question Number 75256 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 75257 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75248 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 75242 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 75230 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 75262 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
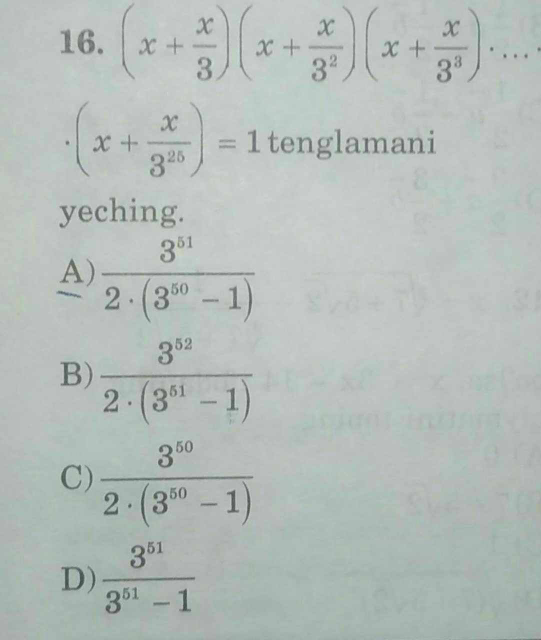
Question Number 75225 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 75224 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 75223 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75222 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
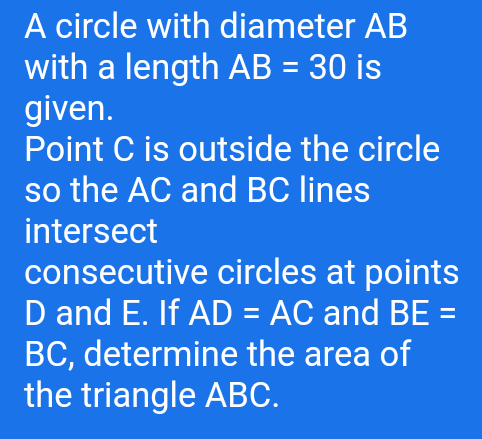
Question Number 75220 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 75228 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 75218 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 75212 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 75208 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75209 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 75204 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75203 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 75193 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Pg 1379 Pg 1380 Pg 1381 Pg 1382 Pg 1383 Pg 1384 Pg 1385 Pg 1386 Pg 1387 Pg 1388
