
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1383
Question Number 75366 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75360 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
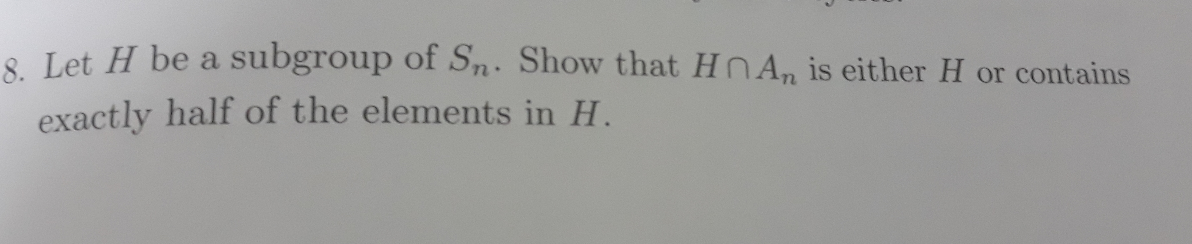
Question Number 75358 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75351 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 75339 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 75330 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 75329 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
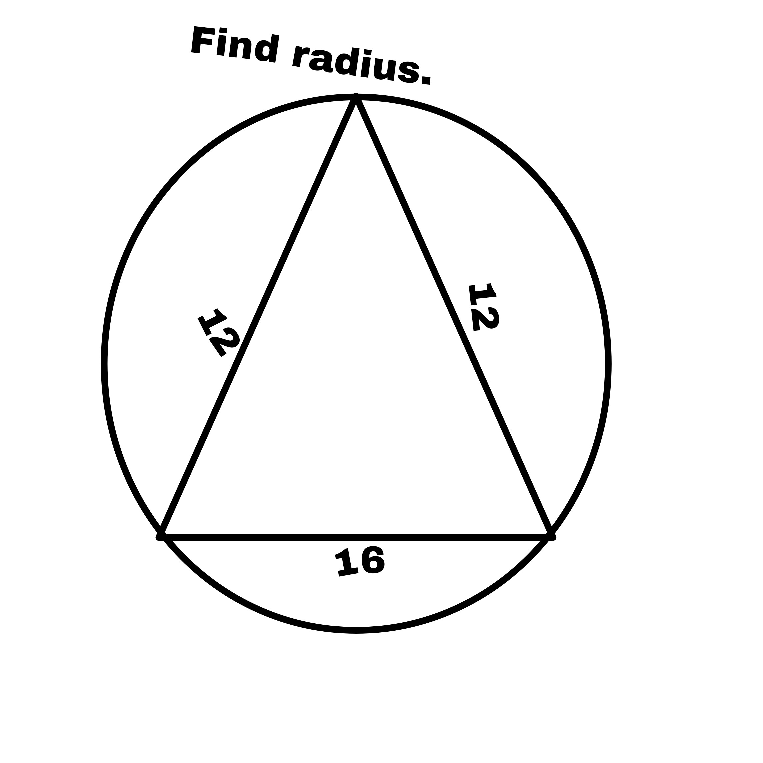
Question Number 75327 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 75325 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 77131 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 75338 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 75321 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 75319 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 75318 Answers: 0 Comments: 6

Question Number 75317 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 75306 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 75303 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75302 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 75301 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 75300 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75299 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 75296 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
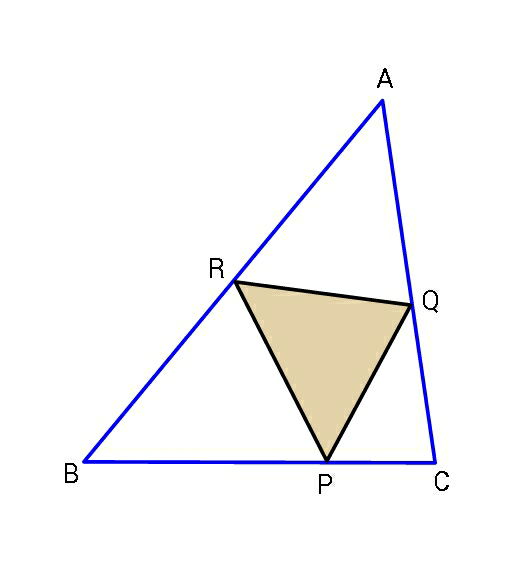
Question Number 75291 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
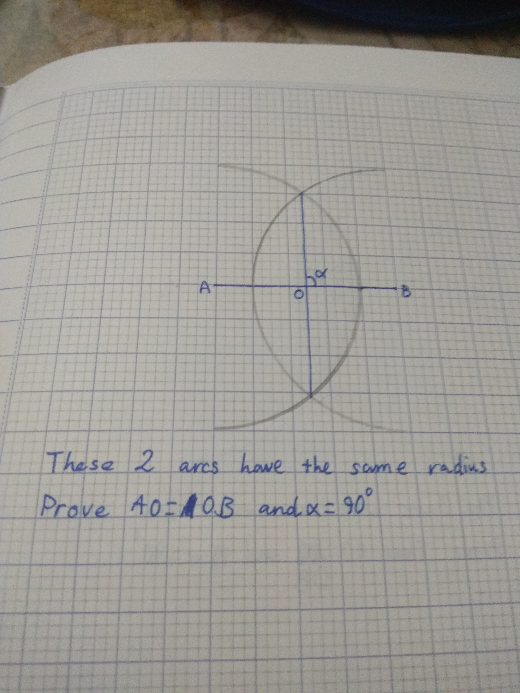
Question Number 75280 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75277 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 75276 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Pg 1378 Pg 1379 Pg 1380 Pg 1381 Pg 1382 Pg 1383 Pg 1384 Pg 1385 Pg 1386 Pg 1387
