
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1339
Question Number 80798 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
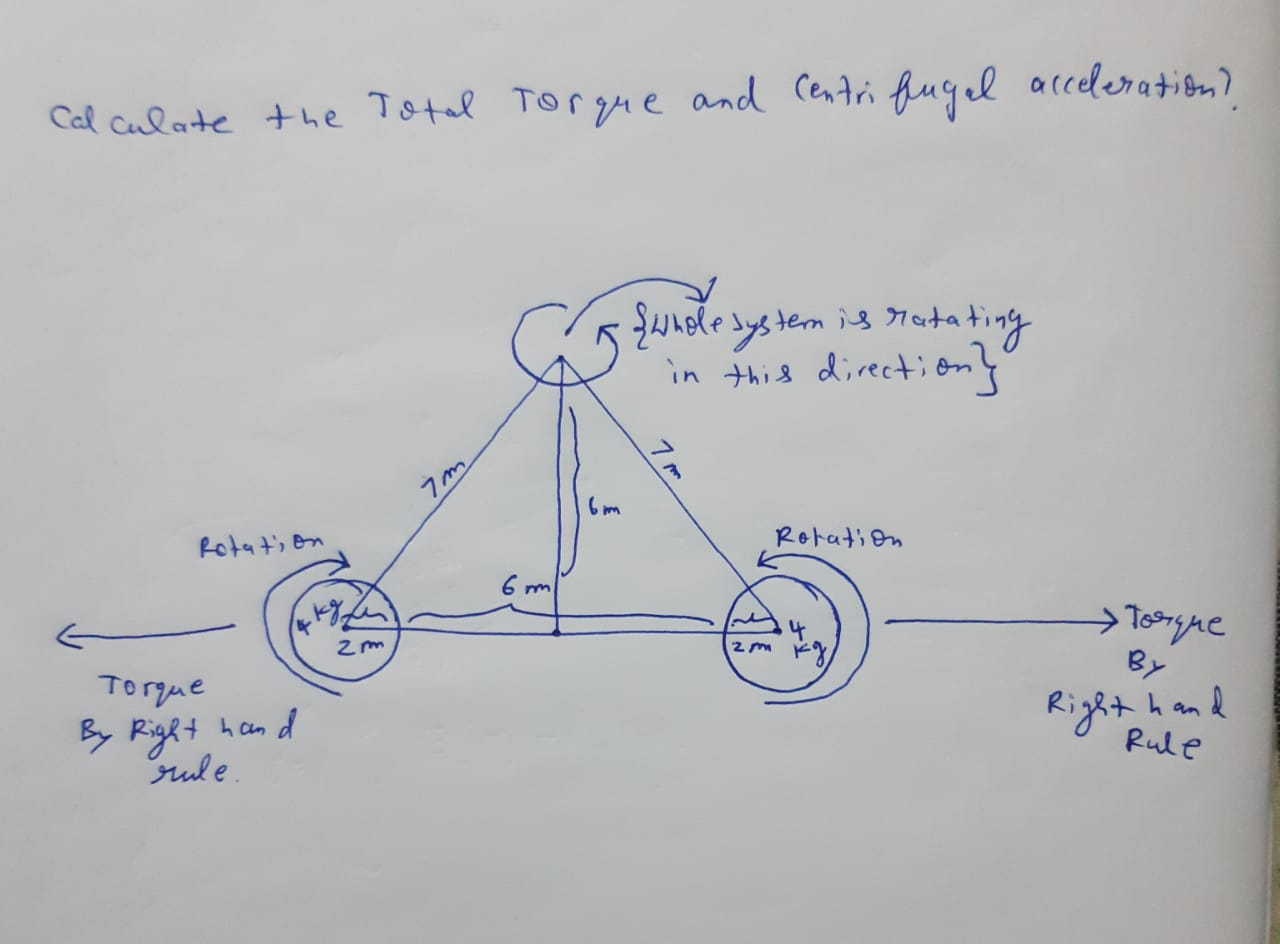
Question Number 80795 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 80792 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 80788 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 80786 Answers: 1 Comments: 5

Question Number 80780 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 80777 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 80775 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 80770 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$$\int\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3x}\:\mathrm{dx}=.. \\ $$
Question Number 80764 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 80761 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 80760 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
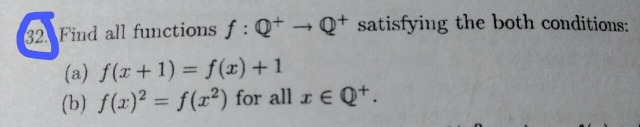
Question Number 80832 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 80752 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 80748 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 80747 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
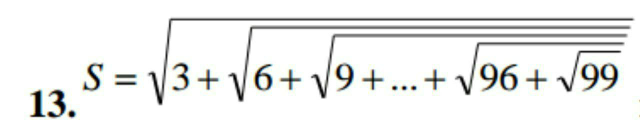
Question Number 80746 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 80739 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 80733 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
$$\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{x}} \Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=? \\ $$
Question Number 80731 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 80718 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 80708 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
Question Number 80706 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 80702 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
Question Number 80690 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 80689 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Pg 1334 Pg 1335 Pg 1336 Pg 1337 Pg 1338 Pg 1339 Pg 1340 Pg 1341 Pg 1342 Pg 1343
