
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1323
Question Number 82726 Answers: 0 Comments: 10
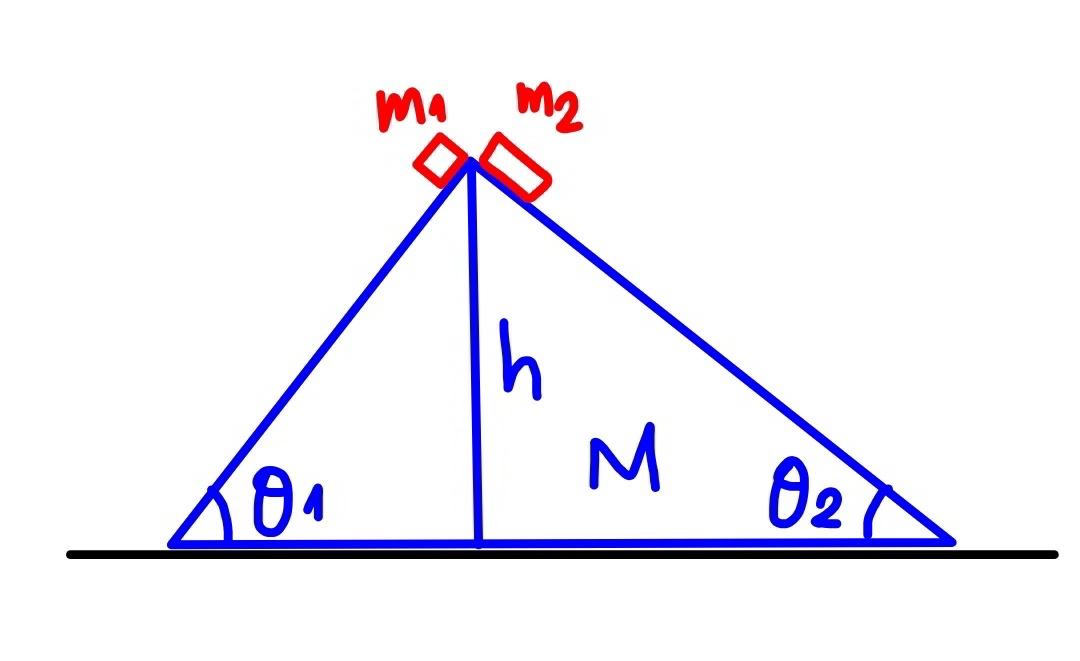
Question Number 82721 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 82719 Answers: 2 Comments: 3
Question Number 82701 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 82700 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{dx}}{\mathrm{3}{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}}}\:? \\ $$
Question Number 82699 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 82687 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 82682 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 82667 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 82665 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 82654 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
Question Number 82647 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 82644 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 82638 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
$${given}\:{x}=\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{3}} {x} \\ $$$${what}\:{is}\:{x}\:? \\ $$
Question Number 82631 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 82628 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 82627 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 82639 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 82617 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{101}{x}\right)\left({sinx}\right)^{\mathrm{99}} {dx} \\ $$
Question Number 82616 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 82614 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 82609 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 82608 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 82607 Answers: 1 Comments: 5

Question Number 82685 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 82604 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1318 Pg 1319 Pg 1320 Pg 1321 Pg 1322 Pg 1323 Pg 1324 Pg 1325 Pg 1326 Pg 1327
