
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1316
Question Number 83477 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${a}^{{b}} +{b}^{{a}} =\mathrm{1}\:\:\:{a}=?\:,\:{b}=? \\ $$$${a}\neq{b}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Question Number 83473 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83471 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 83459 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 83445 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 83441 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83440 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 83430 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83425 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 83492 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 83491 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 83420 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
Question Number 83413 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
$$\mathrm{y}\:=\:\mathrm{x}\:\mid\mathrm{x}\mid \\ $$$$\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{y}\:'\:? \\ $$
Question Number 83411 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
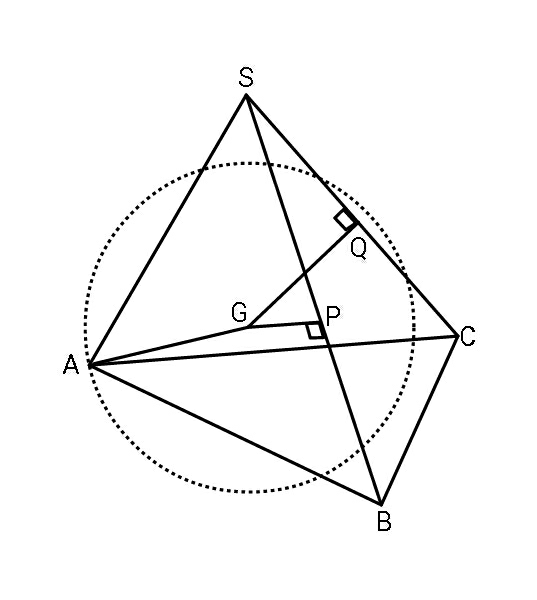
Question Number 83406 Answers: 3 Comments: 3
Question Number 83405 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 83403 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83401 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 83395 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 83385 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 83383 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83381 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 83378 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 83373 Answers: 0 Comments: 4

Question Number 83372 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 83370 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
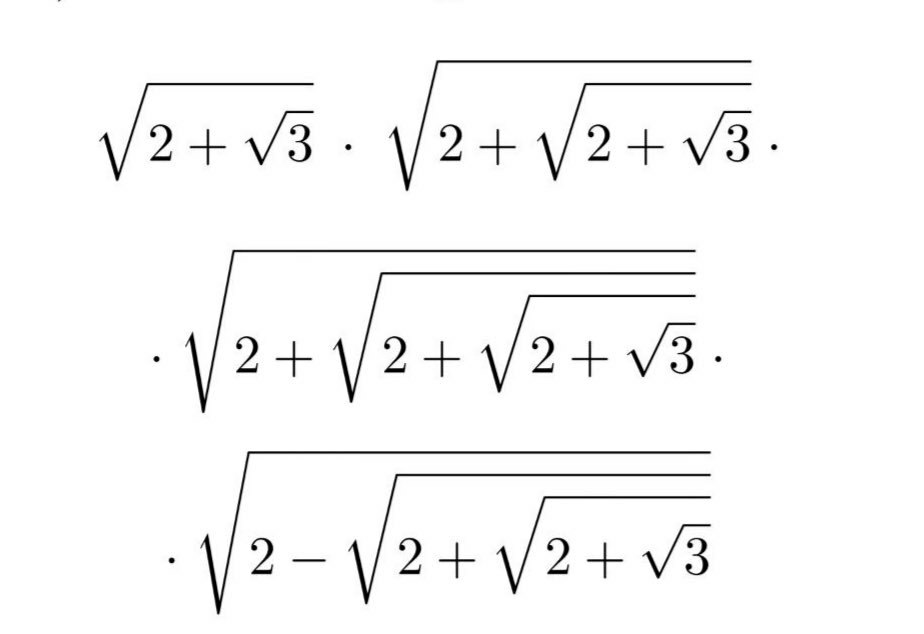
Pg 1311 Pg 1312 Pg 1313 Pg 1314 Pg 1315 Pg 1316 Pg 1317 Pg 1318 Pg 1319 Pg 1320
