
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1311
Question Number 84170 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 84030 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\int\:\sqrt{\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}−\mathrm{3}}}{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 84029 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84021 Answers: 3 Comments: 1

Question Number 84019 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 84018 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 84014 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 84002 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84001 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 84000 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 83999 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 83991 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 83989 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 83984 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 84005 Answers: 2 Comments: 4
Question Number 84004 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
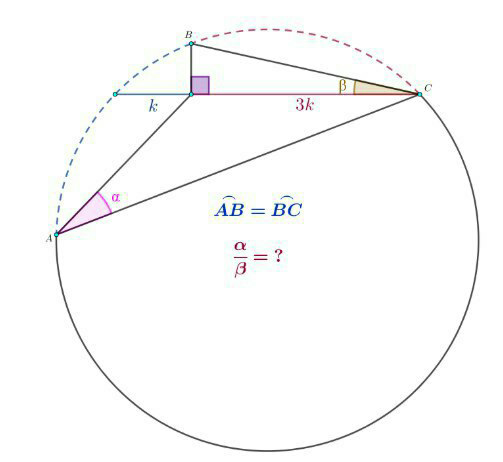
Question Number 83977 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 83975 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 83966 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 83965 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 83964 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83961 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 83960 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 83956 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 83943 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 83941 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1306 Pg 1307 Pg 1308 Pg 1309 Pg 1310 Pg 1311 Pg 1312 Pg 1313 Pg 1314 Pg 1315
