
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1304
Question Number 84628 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 84627 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 84624 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 84607 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
Question Number 84600 Answers: 0 Comments: 9
Question Number 84588 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 84582 Answers: 0 Comments: 10

Question Number 84581 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 84580 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84579 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\int\:\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\sqrt{{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}}{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 84578 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 84577 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 84576 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84575 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84574 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$${calculate}\:\:{I}_{{n}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:{sin}\left({narcsinx}\right){dx} \\ $$
Question Number 84572 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84571 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 84570 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 84569 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${find}\:\:\int\:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{tan}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}} \\ $$
Question Number 84568 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 84566 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 84564 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 84561 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 84558 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 84557 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
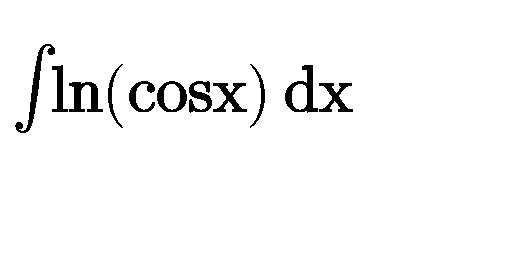
Question Number 84556 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Pg 1299 Pg 1300 Pg 1301 Pg 1302 Pg 1303 Pg 1304 Pg 1305 Pg 1306 Pg 1307 Pg 1308
