
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1265
Question Number 89456 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 89454 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 89451 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 89446 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 89592 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$${cos}\left({x}\right)={k}\: \\ $$$$\left\{−\mathrm{1}\leqslant{k}<\mathrm{0}\right\} \\ $$
Question Number 89596 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 89593 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 89425 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 89422 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 89415 Answers: 1 Comments: 4

Question Number 89412 Answers: 0 Comments: 8

Question Number 89399 Answers: 0 Comments: 11
Question Number 89385 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 89384 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 141569 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 89382 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 89361 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 89351 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 89511 Answers: 1 Comments: 6
Question Number 89510 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
$${Find}\:{the}\:{expansion}\:{of}\:{Xe}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}} \: \\ $$
Question Number 89344 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
Question Number 89343 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 89341 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 89327 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
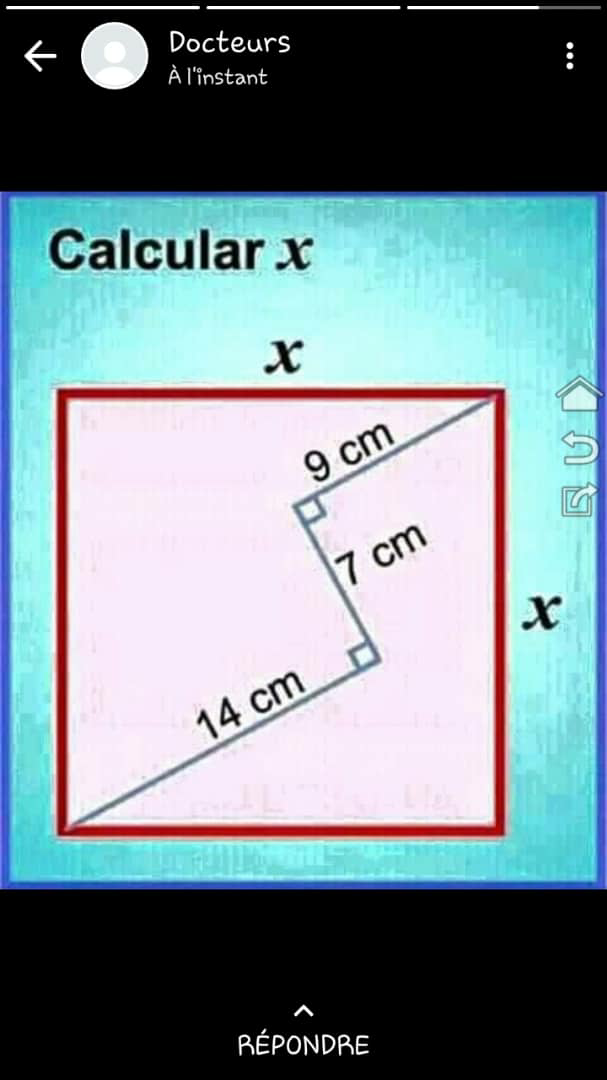
Question Number 89324 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
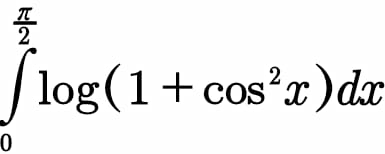
Question Number 89322 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
$$\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{x}} }\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Pg 1260 Pg 1261 Pg 1262 Pg 1263 Pg 1264 Pg 1265 Pg 1266 Pg 1267 Pg 1268 Pg 1269
