
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1260
Question Number 90046 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 90044 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 90043 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 90042 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 90041 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 90040 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 90038 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 90030 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 90024 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 90023 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 90019 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{2467},\:\mathrm{1367}\right) \\ $$
Question Number 90018 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 90013 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$$−{p}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2027}=−{q}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${p}+{q}=? \\ $$
Question Number 90011 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
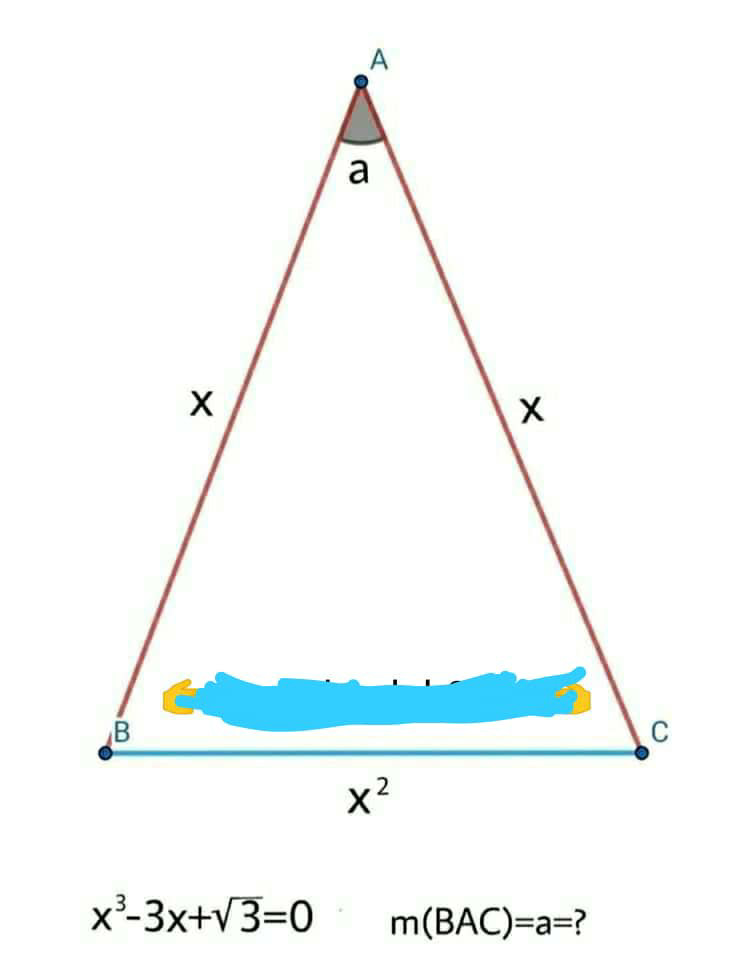
Question Number 90009 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 90003 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 89994 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 89991 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 89986 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 89980 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 89978 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 89977 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
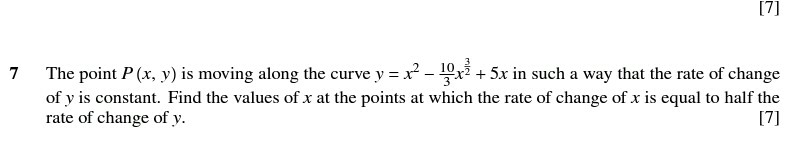
Question Number 89973 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 89970 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 89955 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 89953 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 1255 Pg 1256 Pg 1257 Pg 1258 Pg 1259 Pg 1260 Pg 1261 Pg 1262 Pg 1263 Pg 1264
