
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1249
Question Number 91290 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
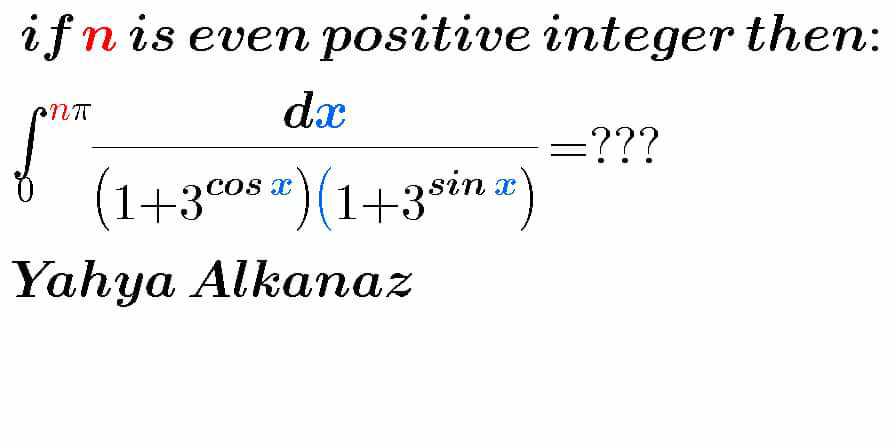
Question Number 91287 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${y}''+\mathrm{2}{y}'+\mathrm{5}{y}=\mathrm{3sin}\:\mathrm{4}{t} \\ $$
Question Number 91277 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 91275 Answers: 0 Comments: 6
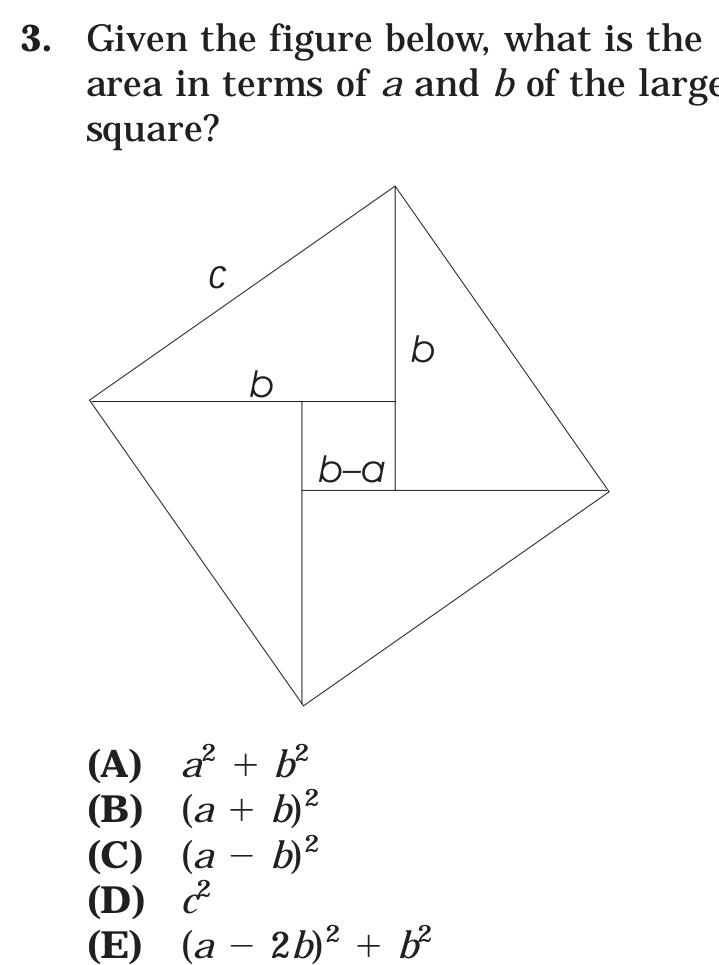
Question Number 91274 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 91272 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\left({D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right){y}\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$
Question Number 91271 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 91270 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 91269 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 91268 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 91263 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 91258 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 92440 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 91230 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 91228 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 91223 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${what}\:{is}\:{complementary}\:{error}\:{function} \\ $$$${erfc}\left({t}\right)? \\ $$
Question Number 91220 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 91217 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 91211 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
$${x}\:{dy}\:+\mathrm{5}{y}\:{dx}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{y}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}\:{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 91196 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 91195 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 91185 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 91183 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
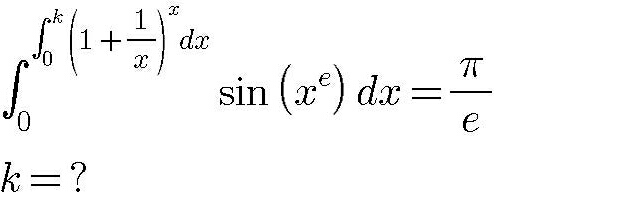
Question Number 91182 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 91178 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 91176 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 1244 Pg 1245 Pg 1246 Pg 1247 Pg 1248 Pg 1249 Pg 1250 Pg 1251 Pg 1252 Pg 1253
