
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1222
Question Number 94649 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$${calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}} {lnx}\:{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 94648 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 94635 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 94632 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 94629 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 94628 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 94625 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 94622 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 94616 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 94609 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 94613 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 94603 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 94602 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 94601 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 94589 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 94581 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 94573 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 94572 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
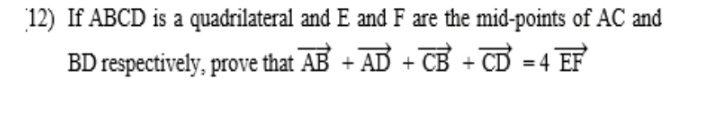
Question Number 94579 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 94559 Answers: 0 Comments: 6

Question Number 94556 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 94553 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{solve}\:\frac{\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid−{x}}{{x}}\:<\:\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$
Question Number 94544 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 94530 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 94528 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
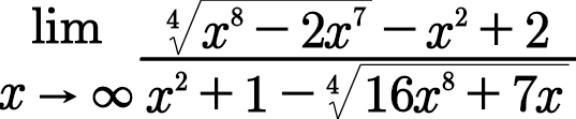
Question Number 94523 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Pg 1217 Pg 1218 Pg 1219 Pg 1220 Pg 1221 Pg 1222 Pg 1223 Pg 1224 Pg 1225 Pg 1226
