
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1208
Question Number 96306 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 96302 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 96296 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 96293 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 96290 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 96289 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$$\mathrm{1010}^{{x}} +\mathrm{2020}^{{x}} =\mathrm{4040}^{{x}} \\ $$$${x}=? \\ $$
Question Number 96287 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 96282 Answers: 3 Comments: 0

Question Number 96280 Answers: 2 Comments: 1

Question Number 96279 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 96276 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 96260 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 96257 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\int\:{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}\:?\: \\ $$
Question Number 96244 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 96242 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 96241 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}^{×} \:\:\:\mathrm{findx}? \\ $$
Question Number 96240 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 96232 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
Question Number 96231 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
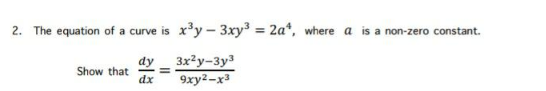
Question Number 96222 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 96220 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
$$\int\frac{{tan}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$\int{x}\:{tan}\left({x}\right)\:{dx} \\ $$
Question Number 96217 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 96211 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 96497 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
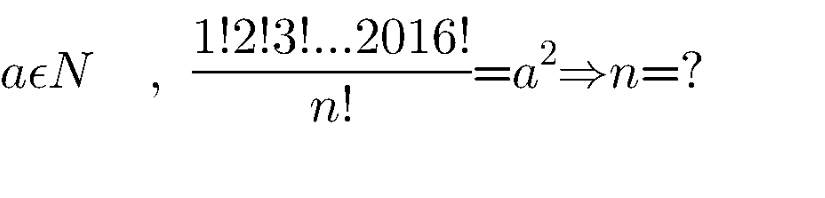
Question Number 96200 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 96198 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1203 Pg 1204 Pg 1205 Pg 1206 Pg 1207 Pg 1208 Pg 1209 Pg 1210 Pg 1211 Pg 1212
